The What So What Now What model is a three-step process that can help you figure out the implications of your goals and take action to achieve them. Borton originally developed this process in 1970 to help people with crisis management, but it can also be used to achieve goals. The What So What Now What model can be used to assess any situation, whether it is personal or professional. You can also use it to assess opportunities as well as crises.
In business, there are three important questions you need to ask yourself: “What do I want?” “So what?” and “Now what?”
The “what do I want” question is about setting goals. The “so what?” question is about figuring out the implications of those goals. The “now what?” question is about taking action to achieve those goals. Below, we will discuss the “so what?” and “now what?” questions in more detail, using the What So What Now What (WSWNW) model.
The What So What Now What Model is a framework that can facilitate reflection, identify areas for improvement, and develop a plan of action. This reflective model can be used in conjunction with other tools, such as the Johari Window and the Critical Incident Technique, to help individuals better understand themselves and the situation they are reflecting on.
Why Use What So What Now What Model?
1. It Can Help You Figure out the Implications of Your Goals
When trying to achieve a goal, it’s important to assess the implications of your actions and develop a plan of action. The WSNW model can help you do this by forcing you to ask questions such as What So what Now what? What does this mean for me/us? What are the consequences? What can I/we do about it?
You want to lose weight. What is the problem or opportunity? You are overweight and want to improve your health. So what? What are the implications of losing weight? This includes assessing the risks and rewards.

2. Helps You Take Action in Response
The WSNW model can also be used to take action in response to a problem or opportunity. This is done by asking questions such as: what happened? Why did it happen? Who was involved? What are the consequences? So what? Now what? What can I/we do about it?
You’ve been laid off from your job. What is the problem or opportunity? You’re out of a job and need to find a new one. So what? What are the implications of being laid off? This includes assessing the risks and rewards.
Some risks might include being unable to find another job, taking a pay cut, and starting over in a new field. Rewards might include: getting a fresh start, finding a better job, and making new connections.
Now what? What is the best course of action? This includes developing a plan of action and considering the risks and rewards you assessed in the previous step. Some actions you might take include: applying for unemployment benefits, networking, and updating your resume.
What So What Now What Templates
The Format of the What So What Now What Model
The WSNW model is typically presented in a linear format, with each question leading to the next. However, it’s important to note that this flexible model can be adapted to fit your needs.
Here’s a basic outline of the What So What Now What model:
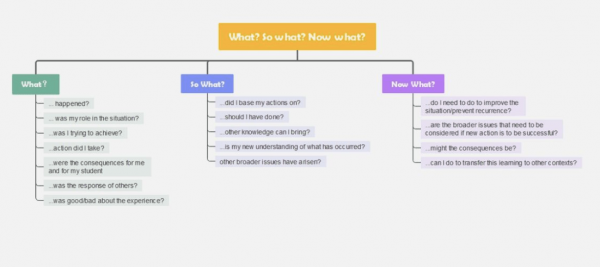
What is the problem or opportunity?
- What is the problem or issue that we are facing?
- What did you notice?
- What was everyone’s reaction to the event?
- What did you learn?
- What part of the experience did you find challenging?
- What did you find surprising?
- What positive and negative aspects do you observe?
- What part of the experience did you find exciting?
So what? What are the implications of this problem or opportunity?
- Why is it important? What critical questions does this information cause us to ask?
- What did this experience make you feel?
- What conclusions can be made from this experience?
- What did you learn about yourself?
- What did you learn about others?
- What emotions does the event evoke? How does it make us feel?
Now what? What is the best course of action?
- How will this experience change your community in the future?
- What do you need to do to address any challenges that arose during this experience?
- What would you like to learn about this experience?
- How will this experience contribute to your career?
- How will you apply what you have learned from this experience?
You can adapt this model by adding additional questions, such as:
Who was involved?
Why did this happen?
What are the consequences?
How to Create What So What Now What Model?
There are four steps to creating a What So What Now What model.
Define the Problem or Opportunity
The first step is to define the problem or opportunity. What are you trying to achieve? What is the goal? For example, you want to start a tech company.
Assess the Risks and Rewards
The second step is to assess the risks and rewards of your goal. This includes looking at both the positive and negative outcomes of your actions. Some risks might include failing to gain traction with users, high competition, and running out of money. Rewards might include making a lot of money, being your boss, and positively impacting the world.
Develop an Action Plan
An action includes figuring out what you need to do to achieve your goal. Some actions you might take include quitting your day job to work on your business full-time, seeking funding from investors, and hiring a team of employees.
Take into account the Risks and Rewards
The fourth and final step is to consider the risks and rewards you assessed in step 2. This will help you figure out if starting a tech company is the right decision for you by forcing you to assess the implications of your decision and develop a plan of action.
Some risks might include failing to gain traction with users, high competition, and running out of money. Rewards might include making a lot of money, being your boss, and positively impacting the world.
Examples of Situations You Can Use This Model
New Business Venture
Before you take the plunge into starting your own business, it’s important to assess the implications of your decision. What are the risks and rewards of starting a business? What are the potential consequences if things don’t go as planned? Using the What So What Now What model can help determine if starting a business is the right decision.
You want to start a tech company. What is the problem or opportunity? You have an idea for a new app that you think could be successful.
So what? What are the implications of starting a tech company? This includes assessing the risks and rewards. Some risks might include: failing to gain traction with users, high competition, and running out of money. Rewards might include making a lot of money, being your boss, and having the potential to impact the world positively.
Now what? What is the best course of action? This includes developing a plan of action and considering the risks and rewards you assessed in the previous step. Some actions you might take include: quitting your day job to work on your business full-time, seeking out funding from investors, and hiring a team of employees.
Considering a New Job Opportunity
Before you accept a new job, it’s important to assess the implications of your decision. What are the risks and rewards of taking this new job? What are the potential consequences if things don’t go as planned? Using the What So What Now What model can help determine if this new job is the right decision for you.
You’ve been offered a new job that pays twice as much as your current job. What is the problem or opportunity? You have been offered a new job with a higher salary.
So what? What are the implications of taking this new job? This includes assessing the risks and rewards. Some risks might include longer hours, more stress, and a higher workload. Rewards might include a higher salary, more responsibility, and the potential for career growth.
Now what? What is the best course of action? This includes developing a plan of action and considering the risks and rewards you assessed in the previous step. Some actions you might take include: accepting the job, negotiating for a better salary, or asking for more information about the job responsibilities.
Considering a New Investment
Before you invest your money, it’s important to assess the implications of your decision. What are the risks and rewards of investing in this company? What are the potential consequences if things don’t go as planned? Using the What So What Now What model can help determine if this investment is your right decision.
You are considering investing in a new tech company. What is the problem or opportunity? You have the opportunity to invest in a new tech company. So what? What are the implications of investing in this tech company? This includes assessing the risks and rewards.
Now what? What is the best course of action? This includes developing a plan of action and considering the risks and rewards you assessed in the previous step.
Other examples of situations include:
• When you are considering a new product launch
• When you are considering a change in your personal life, such as getting married or having a child
Tools of Creating This Model and Sources of Reference
Borton Reflective Model
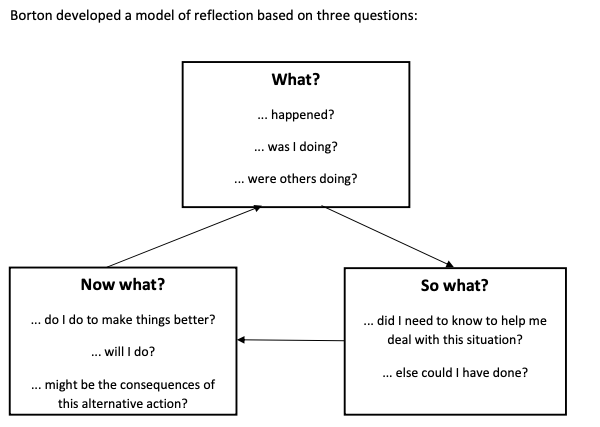
Borton’s Model is a framework that can be used to facilitate reflection. It consists of three questions: “What So what Now what”. The “what” question helps you identify and describe the event or experience you are reflecting on. The “so what” question helps you to explore the meaning of the event or experience and its implications for you. The “now what” question helps you identify what action you need to take as a result of your reflection.
The What-So-What-Now Model
The What-So-What-Now model is a template that can be used to facilitate reflection. It consists of three questions: “What So what Now what”
The “what” question helps you identify and describe the event or experience you are reflecting on. The “so what” question helps you to explore the meaning of the event or experience and its implications for you. The “now what” question helps you identify what action you need to take as a result of your critical reflection.
Johari Window
Another tool is the Johari Window which is a template for self-awareness. This tool consists of four quadrants:
• Open Quadrant
• Hidden Quadrant
• Unknown Quadrant
• Blind Quadrant
The Johari Window can be used in conjunction with the What-So-What-Now model to help individuals better understand themselves and the situation they are reflecting on.
The Ladder of Inference
The Ladder of Inference is a template that can be used to understand how we arrive at our conclusions. It consists of six steps:
• Data
• Assumptions
• Beliefs
• Values
• Conclusions
• Actions
The Critical Incident Technique
The Critical Incident Technique is a framework that can be used to collect data about an event or experience. It consists of four steps:
• Identify the event or experience you want to reflect on
• Gather data about the event or experience from as many sources as possible
• Analyze the data to identify patterns or themes
• Draw conclusions about what happened and why it happened
Driscoll Method
John Driscoll’s reflective model is a reflective model that can be transformed into a structured thought process. There are many reflective models to choose from, so it’s essential to select a model that is appropriate to you.
Driscoll linked the question what? So what? and Now what? at a stage in the experiential learning cycle. Then he included some trigger questions that require answers to complete the reflection cycle. This model is one of the most basic reflection models available to date.
By answering the three questions, you can analyze and learn from your experience.
First, you must describe the situation or experience. Understanding the context is very important.
This allows the person to better understand what is going on. This is achieved by thinking about the “what” question. Do you need to introduce something new? What did you gain from the experience?
The user is prompted to consider the action taken based on the reflection of the last step. Should you change your behavior? Or does it mean that the current state is good enough that no changes are required?
Bain’s 5R’s
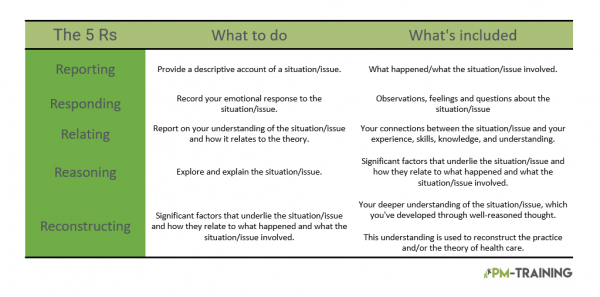
An excellent method to reflect on past experiences is to use a framework that stimulates deep and meaningful thinking about what happened. Learning through experience is just as much about interpreting what has occurred as it is about how we participate in it. Reflecting on past experiences and re-evaluating them is essential for professional and personal growth. One such framework is the 5Rs of reflection. They are Reporting, Reconstructing, Responding, Reasoning, and Relating.
FAQs
What Is Rolfe’s Reflective Cycle?
Rolfe’s reflective cycle is a framework that can be used to facilitate reflection. It consists of three questions: “What So what Now what”
What Is The Use Of What So What Now What Model?
The What So What Now What Model can be used to facilitate reflection, identify areas for improvement, and develop a plan of action.
Who Created The What So What Now What Model?
The What So What Now What Model was created by Borton in 1970
What is What? So what? Now what? Reflection Model?
What, So What? Now, what? are reflecting models that assist you or others in evaluating an experience or a recent occurrence in order to improve or act.
What is the Driscoll method?
The John Driscoll Reflective model is a paradigm for reflection that has been turned into a structured process. There are different other models of reflective thinking, and there’s no one proper choice. It’s critical to select an appropriate model for the participant who will be utilizing it.
What are Bain’s 5 R’s?
The 5R’s reflection is a framework that encourages you to go further into your reflections by prompting you to recognize and understand the relevance of experiences and tasks you’ve completed. It enhances the quality of your post-experience reflections.