At some point in your career as a project manager, you’re bound to be involved in a project management plan that consists in making a quality management system or managing Quality Control Processes. Quality control project management roles are in high demand due to project dimensions’ tedious and detailed nature. Nevertheless, one of the most rewarding things is becoming an expert at it.
Aspiring project managers often ask what quality control measurements are and why they are essential for projects. In this write-up, we try our best to answer these burning questions. Read on to learn more about the quality control process and its measurements so you can confidently accept quality.
- What are Quality Control Measurements?
- Why is Quality Control Measurement Necessary for Projects?
- Benefits of Quality Control Measurements
- How to Plan and Implement Quality Control Measurements
- Quality Control Vs Quality Measurements
- Quality Control Measurements Template
- Quality Measure Checklist
- Project Quality Management Beginners Guide
What are Quality Control Measurements?
Quality control measurements are the output of quality controls. These measurements are the data gathered to assess whether something meets the requirements.
Quality control measurements ensure that products or services meet the necessary standards before being delivered to customers or clients. There are many different types of quality control measurements, but some common ones include:
- Inspections
- Audits
- Testing
- Reviews
Why is Quality Control Measurement Necessary for Projects?
Quality control measurements are essential for a project because they help ensure that the product or service meets the required specifications. They also help identify areas where the product or service does not meet the required specification to take corrective action.
Additionally, quality control measurements help assess whether the project is following its quality management plan. Quality control measurements are vital in any project management situation. Through these measurements, we fully understand the quality control data.
Through these measurements, you can decide whether or not you achieved the correct standard or if there’s a need for any repairs or fixes in the processes.

Benefits of Quality Control Measurements
There are several benefits of using quality control measurements on a project. Some of these benefits include:
- Improvements in product or service quality
- Greater customer satisfaction
- Reduced rework and reduced defects
- Avoidance of costly mistakes
- Increased efficiency of outputs
- Greater compliance with regulations
- Earlier detection of problems
- Enhanced reputation
As you can see, there are many benefits to using quality control measurements on a project. In addition to these benefits, quality control measurements also help reduce the risk of costly errors and improve the chances of meeting deadlines.
How to Plan and Implement Quality Control Measurements
A project manager should know and understand that creating an effective quality management plan involves four steps:
Establishing objectives
The first step in creating an effective quality control program is establishing objectives. This step involves identifying what you need to do to meet the project’s quality goals. Once you have recognized these objectives, you need to develop measurable indicators that you can use to assess whether or not you’re meeting the goals or not.
Planning
The next step is to develop a plan for achieving the objectives you established in step one. This plan should detail how you will accomplish each objective and who will be responsible for each task. Additionally, this step should involve developing resources such as budgets and timelines for each task.
Implementing
The third step is to implement the plan you developed in step two. It involves implementing the plan and ensuring that all tasks are completed as scheduled.
Monitoring and Controlling
The fourth and final step is to monitor and control progress throughout the project with quality audits. This step involves tracking progress against milestones, comparing actual results against objectives, and taking corrective action as needed. By following these four steps, you can create an effective quality management plan that will help ensure your project’s success
Quality Control Vs Quality Measurements
Quality control is the process of ensuring that a product or service meets the standards set by the company. You do it through quality inspections, testing, and other quality-control measures.
When we say quality measurements, this is an actual measurement used to assess whether a product or service meets the necessary standards. This can be done through surveys, customer feedback, and other quality-measurement tools.
The quality control process ensures that products and services meet the company’s standards. However, quality measurements are necessary for assessing whether those standards are met.
And to add, just in case you’re wondering, quality assurance is the maintenance of the desired output quality towards every stage of the delivery process or production line.
Quality Control Measurements Template
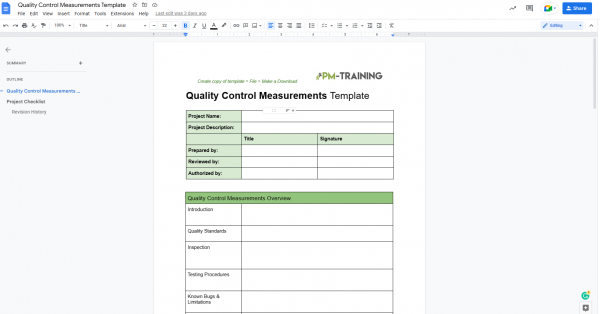
Quality Measure Checklist
A comprehensive quality measurement checklist can help organizations evaluate their software products and identify areas that need improvement. For example:
- User Experience: A software product with a poor user experience can lead to decreased engagement, decreased adoption, and decreased satisfaction. User experience can be evaluated based on factors such as ease of use, accessibility, intuitiveness, and user-centered design.
- Functionality: Functionality refers to the ability of the software to perform the intended tasks. It can be evaluated based on factors such as the completeness of the software’s features, the ability to perform tasks in a timely manner, and the ability to perform tasks correctly.
- Performance: Performance is a crucial aspect of software quality as it affects the user experience. Performance can be evaluated based on factors such as speed, responsiveness, and stability.
- Security: It can be evaluated based on factors such as data protection, privacy, and secure access to the software.
- Code quality: Code quality refers to the organization and structure of the code. It can be evaluated based on factors such as readability, maintainability, and test coverage.
- Scalability: Scalability refers to the ability of the software to grow and support larger numbers of users. Scalability can be evaluated based on factors such as the ability to add new features and the ability to handle increased traffic.
- Compatibility: Compatibility refers to the ability of the software to work with other software and hardware. It can be evaluated based on factors such as compatibility with different operating systems, compatibility with different browsers, and compatibility with different devices.
- Maintenance: It refers to the ongoing work required to keep the software up to date and functioning properly. It can be evaluated based on factors such as the availability of support, the frequency of updates, and the responsiveness of the development team.
- Documentation: Refers to user manuals and technical documentation. It can be evaluated based on factors such as accuracy, completeness, and accessibility.
By considering each of these factors, organizations can identify areas for improvement and work towards creating high-quality software that meets the needs of their users.
FAQs
What are the four types of quality control?
There are four types of quality control: process control, acceptance sampling, control charts, and product quality control.
1. Process Control: It uses feedback to monitor and adjust processes to produce the desired results.
2. Acceptance Sampling: It is a quality control method in which a sample of products is inspected to determine if it meets the quality standards set by the company.
3. Control Charts: They are graphical tools used to monitor process stability and control.
4. Product Quality Control: It is the inspection of products to ensure that they meet the quality standards set by the company.
What are the three main objectives of quality control?
The first step of quality control is to establish objectives. This step involves identifying what needs to be done to meet the project’s quality goals. Once you have recognized these objectives, you need to develop measurable indicators you can use to assess whether or not you met the goal.
What is a quality control checklist?
A quality control checklist is a guide that contains instructions for inspectors to follow when they are checking products. The written guide includes content about the product, packaging, color, barcodes, and appearance. It also covers possible defects of the function and any special requirements.
What are the three levels of quality?
The Three levels of quality are acceptable quality, which is the minimum level of quality acceptable to the customer; appropriate quality, the level of quality that meets the customer’s expectations and aspirational quality, the highest level of quality that a company can aspire to achieve.
What are the seven principles of quality management systems?
1. Customer focus
2. Leadership
3. Engagement of people
4. Process approach
5. Improvement
6. Evidence-based decision making
7. Relationship management
What are the four main elements of quality?
Quality management has four main areas: quality control, quality improvement, quality planning, and quality assurance. Its focus is not only on the product or service itself but also on how to achieve optimal results.
