Project planning is the discipline that addresses how to complete a project in a given period, usually with designated resources and defined stages. The activity can be divided into the following steps:
- Planning tasks
- Setting objectives
- Scheduling
- Deliverables identification
What are the components of a project plan?
There are three main parts of a project plan. They are budget, scope, and timeline and comprise the following aspects:
- Scope. The scope indicates what the project team will not do and what it will do. It takes the customer’s requirements and the team’s vision and determines the possibilities. Setting performance goals and part of defining the project scope and the project manager must consider this.
- Budget. Project managers determine the resources and manpower required to achieve the project goal and estimate the cost of a project.
- Timeline. This includes the time required to complete each project phase and the schedule of milestones to be met.

Why is project planning important?
Project planning is crucial at each project phase. It sets the following basics of a project:
- Objectives
- Scope
- Schedule
- Goals
Planning facilitates the project managers in turning an idea into reality. The main purposes of planning are:
- To help the key stakeholders and project sponsor know the requirements
- To provide information and facilitate communication for project personnel
- To identify when, how, and who will perform certain tasks
- To facilitate project control and management
- To facilitate project monitoring and control
- To manage project risks
- To generate feedback that will facilitate the next phases of the project
How do you create a project plan?
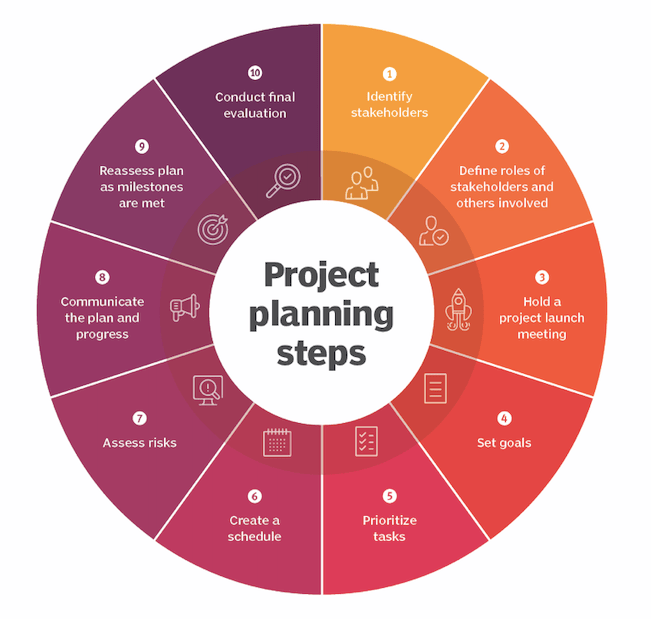
You can create an effective project management plan by following these 10 steps.
Define stakeholders
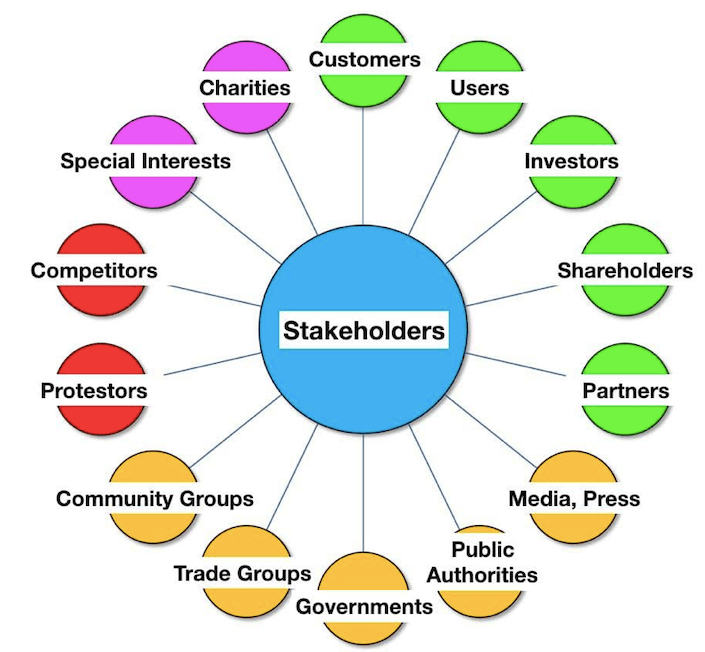
Stakeholders are the entities that have an interest in the project. They include the end-user or the customer, project team members, people affected by the project in the organization and outside the organization, and individuals that have an interest in the project. Examples of stakeholders include customers, employees, shareholders, and suppliers. Some of these stakeholders are internal to the organization i.e the employees and the shareholders. Others, such as suppliers and customers are external to the organization but are affected by the project.
Define roles
Define the role of each stakeholder clearly. Some stakeholders will assume multiple roles. Examples of roles are project manager, project sponsor, team member, and team leader.
Introduce stakeholders
Unify the vision and bring the stakeholders together by holding a meeting. The topics covered should include goals, scope, role, budget, and schedule
Set goals

Take what is obtained from the meeting and develop it into a plan. It should include deliverables and goals that define what the service or product will deliver. Examples of goals are improving collaboration and communication and improving performance and productivity.
Prioritize tasks

Make a list of tasks required to achieve goals and prioritize them based on interdependencies and importance. A Gantt chart can help in mapping dependencies.
Create a schedule
Create a timeline and consider the resources required for the tasks. An example of creating a schedule is to list each task, assign team members, and set due dates.
Assess risks
Identify risks in the project and develop mitigation strategies. An example is health and safety risk where the safety manager determines the risks associated with the work environment, job, and processes.
Communicate
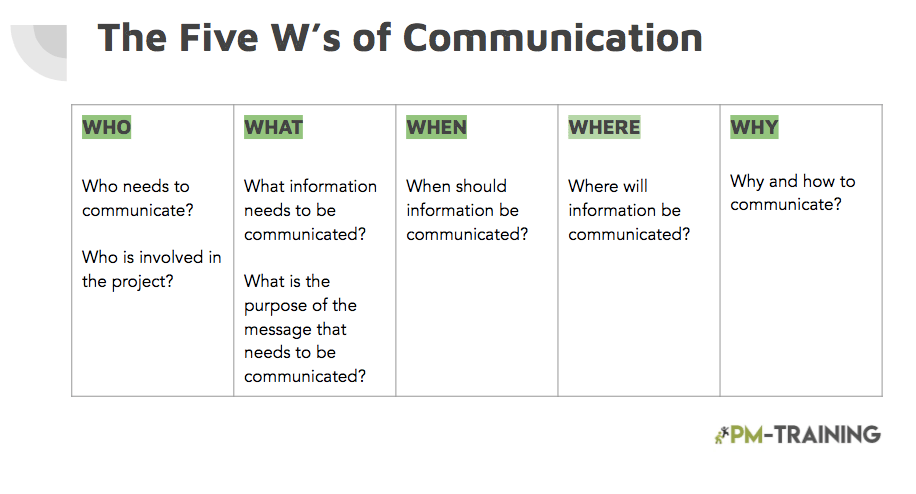
Provide communications updates and share the plan with the stakeholders in a frequency and format that they expect. Some examples of the communication step include deciding on the communication methods and types, communication style, and meeting schedules.
Reassess
As milestones are achieved, revisit the plan and revise areas that do not meet expectations.
Final evaluation
After the project completion, evaluate the performance to identify areas to improve and to learn from experience. An example of a final evaluation is giving the project sponsor information about the actual and target comparison of the project.
.
What are some project planning tools and software?
The project planning process is facilitated by project management and project planning software. The best tools have intuitive user interfaces, support collaboration, and provide built-in invoicing and time tracking.
Some of the software tools for project planning include:
- Asana offers several project views that suit the project team’s preferences.
- ClickUp has many Agile-based features, including a custom automation builder to let users create reusable task templates.
- Freedcamp allows users to organize projects using Kanban or Gantt charts.
- Hive has a task management feature that allows the creation of a template and speeds up the creation of the task.
- Trello provides budget management, Kanban features, progress tracking, and resource management features.
- You can download the free project planning template here
- Step-by-step guide for project planning template in word and excel
What are the 5 characteristics of a project plan?
5 characteristics of a well-defined project plan are:
- Specific: The project should be specific
- Measurable: The project must be measurable in terms of achievements and benefits
- Achievable: The project can only make sense if it is achievable
- Relevant: The project must be beneficial to the concerned entity
- Time-bound: The project must be time-bound
- To learn more about project planning techniques click here
What are the 10 project planning steps?
The 10 project planning steps are:
- Define stakeholders
- Define roles
- Introduce stakeholders
- Set goals
- Prioritize tasks
- Create a schedule
- Assess risks
- Communicate
- Reassess
- Final evaluation
