Project estimation techniques assist project managers in effectively estimating crucial project components like cost and scope. These methods can also be used in Agile IT operations to allocate resources effectively.
Project Managers can more properly budget the money and resources they require for a project’s success thanks to these project estimation methodologies, which also enable them to give clients better forecasts.
Project estimates can be created using project estimation methodologies. These methods assist you in coming up with a reasonable estimate to provide to your customer or another project stakeholder when they ask you to estimate a certain project component.
Planning your project is impossible without correct project estimates. There is no way to guarantee you’ll have the appropriate staff, materials, or tools on hand when you need them if you don’t know how long the job will take or how much it will cost.
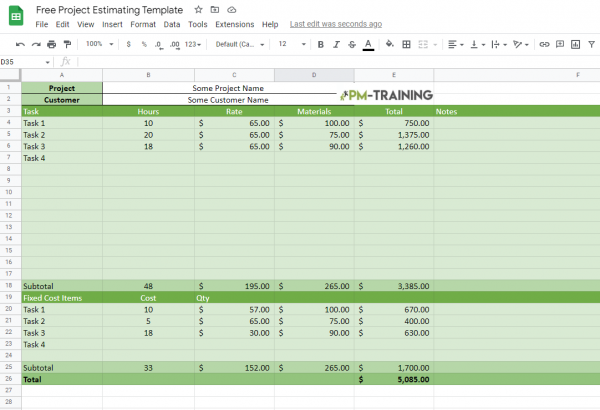
Free Project Estimating Template
Parametric Estimation
Parametric estimation is a project estimation technique where you use mathematical models to estimate the cost, schedule, or scope of a project. This can be a powerful tool for project managers, as it can help to reduce uncertainty and improve the accuracy of estimates.
Why is it important?
First, it can produce more accurate results than other estimation techniques. Secondly, it can be used to account for known risks and uncertainties. Third, it can be used to generate “what if” scenarios to help project managers plan for potential problems.
Advantages and disadvantages of Parametric Estimation
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| It can be helpful in budgeting and planning for future projects. | The most important challenge is that the models used for estimation are often complex and require expert knowledge to use. |
| It can be very accurate when the data is right | It is only as good as the data that is used to create the models. If the data is inaccurate, the estimates will also be inaccurate. |
| Makes it easy to compare different options | Requires data and assumptions that may not be available |
| Can be used for projects of all sizes | It may not be accurate if the project is very complex or unusual |

When to use Parametric Estimation
As it can also be used to predict future costs or durations, it can be helpful in budgeting and planning for future projects for your next project.
This technique is often used in engineering and construction projects
When not to use Parametric Estimation
When the project is very new and there is not enough information to create a reliable model
When the project is very complex and there are many variables that cannot be accurately captured in a model
When the project is very small and the extra effort required to create a parametric model is not worth it
Bottom-up Estimating
Project bottom-up estimation technique, you start with the smallest unit of work and then estimate the cost of each individual unit. Once you have the cost of all the units, you can then add them up to get the total overall cost of the project.
Why is it important?
In project management, this method provides a more accurate estimate of the project’s true cost. This is because bottom-up estimating takes into account all of the project’s individual components and their costs.
At this point, it can massively help you to identify potential risks and issues early on in the project, which can save time and money in the long run.
Advantages and disadvantages of Bottom-up Estimating
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| You can get more highly accurate estimates by starting with the individual components | It can be time-consuming to gather all of the detailed information needed for the estimate |
| This approach can be helpful in situations where there is a lot of detailed information available. | This approach can be less accurate than other types of estimation if you don’t have complete information about all of the components which means you can err highly if that happens. |
| It can help you to avoid cost overruns and ensure that projects stay on budget. | The extra effort required is not that easy when estimating the cost of some of the smaller units. |
When to use Bottom-up Estimating
This approach can be helpful in situations where you have a lot of detailed information about the individual parts of the project.
When not to use Bottom-up Estimating
When you have a project with a short timeline. This is because it may not be worth spending that time with every detail of every unit. Therefore, it can be time-consuming for your team.
Analogous Estimating
Analogous project estimation technique can be useful when there is limited data available about the new project, or when the new project is similar to past projects in terms of scope, complexity, or other factors.
Why is it important?
Considering that few data and resources in project management analogous estimating is considered to be the most reliable and quite helpful, especially if you need to communicate to your team and stakeholders a wide overview of the project by giving decision-makers a starting point for budgeting and planning purposes

Advantages and disadvantages of Analogous Estimating
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Some of the advantages include the fact that it is quick and easy to do | Some of the disadvantages include the fact that it can be inaccurate, and it may not be appropriate for all projects |
| it can be useful when there is limited information about the current project | A drawback is the fact that it can be inaccurate if the analogy is not close enough, and it does not take into account the unique aspects of the new project. |
When to use Analogous Estimating
If you have a project that is similar to ones that have been done in the past, it may be a good option to use
when there is a need to quickly estimate the cost or time required for a project
When not to use Analogous Estimating
If the project being estimated is very different from any other project that has been completed, then it is not an appropriate candidate for this estimation technique.
If the project is very large or complex, it may also be difficult to accurately estimate using this method.
When the data from previous projects is of poor quality or the team is inexperienced.
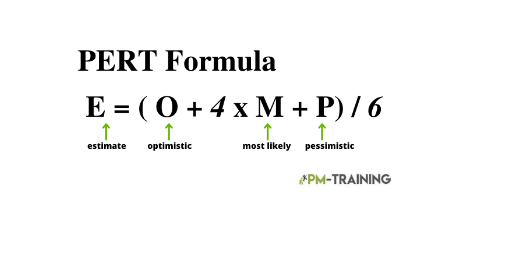
PERT Formula estimating
The PERT estimating formula is a statistical tool used to predict the outcome of an activity or task. As a Beta distribution technique (different from Triangular) it is often used in project estimations to estimate the amount of time needed to complete a project.
In PERT, there are four ways to define time:
The shortest amount of time necessary to perform a task is called the optimistic time.
Pessimistic time: The longest amount of time necessary to finish a task.
Most likely time – The amount of time that should be required to finish an activity, according to a plausible assessment.
Most likely time – The most accurate estimation of the amount of time needed to finish a task.
Why is it important?
It forecasts project completion dates while taking unpredictability into account. It also enables the project manager, who is frequently in charge of planning and managing a number of intricate tasks and activities, to keep track of how a project is coming along.
Advantages and disadvantages of PERT
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Its ability to account for uncertainty | It can be potentially inaccurate |
| It is helpful when you need to keep track of the progress of your project | Its full reliance on estimations makes it delicate in the case is not properly calculated |
| The coordination of project activities and departmental communication can both be made better with the assistance of the qualitative and quantitative data gathered from these numerous sources. | Its main drawback is that it frequently underestimates duration rather than accurately estimating it or overestimating it. |
When to use PERT
When you need to Identify the essential path for the project to ensure that all deadlines are reached
whenever the project manager must show the various task interdependencies
when the project manager must determine how long the project will take to finish; and get ready for increasingly difficult and substantial tasks
When not to use PERT
if the project is very small or if the timeline is very tight, the PERT formula may not be the best option. In these cases, a more simplified approach may be more effective.
For projects that are only a few hours or days long, the PERT formula is not likely to be accurate.
The PERT formula should not be used if the project is very complex. If the project has many interdependent tasks, this formula may not be able to capture all the potential impediments to completion
3 Point estimation
3 point estimation technique well known as Triangular distribution is a simple average popular project management tool used to schedule, organize, and control projects. It is based on this formula E=(O+M+L)/3 and it follows these three values:
The optimistic estimate (O), which is the best-case scenario
The pessimistic estimate (P), which is the worst-case scenario
The most likely estimate (M), which is the most likely scenario
Why is it important?
A three-point estimation can make your work simpler and more precise even if many project managers consider project estimate calculation to be one of their most difficult responsibilities.
Advantages and disadvantages of 3 Point estimation
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| It forces you to think about the uncertainty of your estimate | It can be time-consuming |
| It is easy to understand and use | It won’t work in every situation. Despite the fact that it works best in huge projects, it typically also calls for higher team member engagement. |
| It provides a range of possible outcomes | It can lead to overconfidence in the accuracy of the estimate. |
When to use 3 Point estimation
This technique is often used early on in the project planning process before more specific details are known. This allows for a more broad estimate of the project’s potential outcomes.
It is particularly useful when there is uncertainty about the project or when the project has a large scope
When not to use 3 Point estimation
if you are dealing with a very simple task that has a low level of uncertainty, then this technique may not be necessary
if you are dealing with a very complex task that has a high level of uncertainty, then this technique may not be accurate
Rough Order of Magnitude (ROM)
Without going into great detail, Rough order of magnitude (ROM) is a technique used in project management to estimating the order of magnitude of a project cost, schedule, or quantity. This is used during the initial phase of project estimations.
Why is important?
In general terms, ROM can give your team a quick and efficient overview of how things are going to go. Therefore everyone will have a general idea about when and how to start the project more productively.
Advantages and disadvantages of ROM
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Quick and easy to produce and it can provide a good starting point for more detailed estimates | It is often way less accurate than other types of estimates |
| You will be able to estimate the project cost, schedule, or scope in a wide range | It can lead you to unrealistic expectations. Basically, give you a false sense of precision |
| It can be helpful when doing comparisons between project’s options | It does not consider the impact of uncertainty |
When to use ROM
This type of project estimation is often used early in the project planning process
ROM should only be used when there is a high degree of uncertainty surrounding the project
When not to use ROM
When high accuracy is required
When the project is very well understood and there is little uncertainty
If you’re estimating the cost of a new product, you’ll want to be as accurate as possible to avoid overspending. Therefore it is not recommendable to use ROM.
FAQs
Which method of project estimation is the most accurate?
The most accurate method of project estimation is the Bottom-up approach.
What is the difference between analogous and parametric estimating?
Analogous estimating is based on the cost of similar projects, while parametric estimating is based on the statistical relationship between variables.
Which is the least time-consuming project estimation technique?
Analogous Estimating is the least time-consuming project estimation technique
