We go through the mistakes 80% of people make which leads them to fail the PMP on their first try, highlight appropriate study material and a complete study plan for you to follow.
I made the costly mistake of only reading the PMBOK® Guide the first time around and wasn’t till after failing that I learned how much of a rookie mistake it was. The PMBOK® Guide is a manual/guide on the PMI® approach to project management and the PMP exam is based on it.
This study guide is really just a snippet of my pdf which you can download by submitting the email address below. I cover everything here and all the essential PMP posts on my blog with one huge secret revealed about my classroom experience.
80% of people who fail the first time will solely rely on the PMBOK for theory PMP preparation. If you take away one thing is that DO NOT SOLELY RELY ON PMBOK to pass the exam. Let me explain.
Tips to Pass PMP Exam 1st Try
1. Get a PMP Study Guide
“Fail to Prepare, Fail to Prepare” is definitely the case when it comes to passing the PMP® Preparation. Get a study guide in terms of a book, course, pdf – anything that is focused on passing the exam will help.
What you need to know is….
Back in 2016 I purchased a study book How to Pass PMP on First Try by Andy Crowe who doesn’t actually have an update to date version so I now recommend….
The leading study book comes from Rita Mulcahy who is on her 11th edition of PMP Exam Prep at time of writing this so ignore the lack of reviews – this lady knows what she is talking about and has helped thousands of people pass the exam.
The highest-rated book on Amazon by Andrew Ramdayal PMP Exam Prep Simplified which includes a free video course so little wonder it was 1,400+ ratings.
2. Use a PMP Exam Simulator
Why is this important? The PMP exam old pattern was based on the traditional phase-based approach but now, it is modified to a domain-based approach. The new exam has seen the inclusion of Agile methodology. There are not many places online you can test yourself on these.
The PM Prepcast simulator is the best online and makes you feel confident of passing the PMP exam as we practice the mock test in the real exam environment. The more you practice better are the chances of getting success. You can read our full review of PM Prepcast Exam Simulator with a discount code here.
3. Have Exam Day Plan
Removing every single unknown of where to park, what you going to eat for lunch, when to take a toilet break, what you need to bring with you, and what to wear for comfort might sound trivial but they will bring a sense of calm to the day of the exam. I have shared my entire pmp exam day plan here.
4. Take as Many PMP Exam Simulators As Possible
When taking exams try to recreate the exam experience by setting aside 2-3 hours with no access to phone or internet. Take scheduled breaks which we outlined in the exam day plan.
PM-Training.net (200Q) This is our very own exam created after I actually did the exam so I tried to include as many exam question topics as much as I could. I tried to cover everything from the above study lists so please leave me know what you think in the comments section after you complete the practice exam.
Oliver Lehmann (100Q) Really difficult test but helped me identify new definitions and areas I hadn’t previously heard about. Oliver Lehmann was one the first to create a PMP practice exam online and has been teaching project management principles for over 10 years. Oliver also has a LinkedIn group well worth joining.
Exam Central (200Q) This was one of my favorite test exams due to the feedback provided. It breaks down answers by process groups so you know where your weakness are to focus on. I only took this exam once due to time constraints but it identified that I was very weak in the initiation process group so I focused more on it and ended up getting Proficient in the area.
PM Study (200Q) Great simulator for emulating the actual exam and good indicator on your ability to pass the real exam. You can also get a second free exam by using their referral system and sharing within your networks. (You can easily just create other accounts with the referral link which will give your original account access to the second exam).
PM Exam Simulator (200Q) A really good simulator with good feedback. This is a good exam to practice your exam strategy and taking advantage of the good simulator.
Head First PMP (200Q) Not the most difficult test but is a complete 200 question exam which helps gauge your level. I did the test with the book and online, the book is a great way of learning fundamentals.
Tutorials Point (150Q) Has some repeat questions and not extremely difficult. Tutorial Point also provide a comprehensive study material people find useful which is worth checking out.
PM Exam Coach (120Q) Free trial test account for 7 days with practice questions for the 2021 exam version.
PMTraining (10Q) Free questions dedicated to the 2021 exam version
PM PrepCast (120Q) Offers practice questions for the 2021 PMP exam version
PMAspire (400Q) Free practice questions with 2021 PMP exam version
Eduhubspot (100Q) PMP practice questions following the 2021 Exam content outline
ProMock (24Q) One of the 2021 PMP Exam edition simulator to test your PMP Exam readiness.
5. Know the PMP Study Material per Domain
The exam questions per be categorized according to the below table:
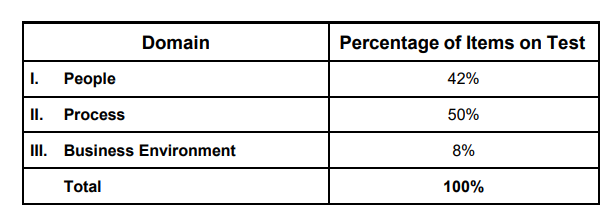
Each domain consists of tasks and enablers. Understanding what is

Domain 1 – People 42%
| ID | Task | Enablers |
| 1 | Manage conflict | – Interpret the source and stage of the conflict – Analyze the context for the conflict – Evaluate/recommend/reconcile the appropriate conflict resolution to avoid a lose-lose solution 2Lead a team- Set a clear vision and mission |
| 3 | Support team performance | – Appraise team member performance against key performance indicators – Support and recognize team member growth and development – Determine appropriate feedback approach – Verify performance improvements |
| 4 | Empower team members and stakeholders | – Organize around team strengths – Support team task accountability – Evaluate demonstration of task accountability – Determine and bestow level(s) of decision-making authority |
| 5 | Ensure team members/stakeholders are adequately trained | – Determine required competencies and elements of training – Determine training options based on training needs – Allocate resources for training – Measure training outcomes |
| 6 | Build a team | – Appraise stakeholder skills – Deduce project resource requirements – Continuously assess and refresh team skills to meet project needs – Maintain team and knowledge transfer |
| 7 | Address and remove impediments, obstacles, and blockers for the team | – Determine critical impediments, obstacles, and blockers for the team – Prioritize critical impediments, obstacles, and blockers for the team – Use network to implement solutions to remove impediments, obstacles, and blockers for the team – Re-assess continually to ensure impediments, obstacles, and blockers for the team are being addressed |
| 8 | Negotiate project agreements | – Analyze the bounds of the negotiations for agreement – Assess priorities and determine ultimate objective(s) – Verify objective(s) of the project agreement is met – Participate in agreement negotiations – Determine a negotiation strategy |
| 9 | Collaborate with stakeholders | – Evaluate engagement needs for stakeholders – Optimize alignment between stakeholder needs, expectations, and project objectives – Build trust and influence stakeholders to accomplish project objectives |
| 10 | Build shared understanding | – Break down situation to identify the root cause of a misunderstanding – Survey all necessary parties to reach consensus – Support outcome of parties’ agreement – Investigate potential misunderstandings |
| 11 | Engage and support virtual teams | – Examine virtual team member needs (e.g., environment, geography, culture, global, etc.) – Investigate alternatives (e.g., communication tools, colocation) for virtual team member engagement – Implement options for virtual team member engagement – Continually evaluate effectiveness of virtual team member engagement |
| 12 | Define team ground rules | – Communicate organizational principles with team and external stakeholders – Establish an environment that fosters adherence to the ground rules – Manage and rectify ground rule violations |
| 13 | Mentor relevant stakeholders | – Allocate the time to mentoring – Recognize and act on mentoring opportunities |
| 14 | Promote team performance through the application of emotional intelligence | – Assess behavior through the use of personality indicators – Analyze personality indicators and adjust to the emotional needs of key project stakeholders |
Domain 2 – Process 50%
| ID | Task | Enablers |
| 1 | Execute project with the urgency required to deliver business value | – Assess opportunities to deliver value incrementally – Examine the business value throughout the project – Support the team to subdivide project tasks as necessary to find the minimum viable product |
| 2 | Manage communications | – Analyze communication needs of all stakeholders – Determine communication methods, channels, frequency, and level of detail for all stakeholders – Communicate project information and updates effectively – Confirm communication is understood and feedback is received |
| 3 | Assess and manage risks | – Determine risk management options – Iteratively assess and prioritize risks |
| 4 | Engage stakeholders | – Analyze stakeholders (e.g., power interest grid, influence, impact) – Categorize stakeholders – Engage stakeholders by category – Develop, execute, and validate a strategy for stakeholder engagement |
| 5 | Plan and manage budget and resources | – Estimate budgetary needs based on the scope of the project and lessons learned from past projects – Anticipate future budget challenges – Monitor budget variations and work with governance process to adjust as necessary – Plan and manage resources |
| 6 | Plan and manage schedule | – Estimate project tasks (milestones, dependencies, story points) – Utilize benchmarks and historical data – Prepare schedule based on methodology – Measure ongoing progress based on methodology – Modify schedule, as needed, based on methodology – Coordinate with other projects and other operations7Plan and manage quality of products/deliverables- Determine quality standard required for project deliverables – Recommend options for improvement based on quality gaps – Continually survey project deliverable quality |
| 8 | Plan and manage scope | – Determine and prioritize requirements – Break down scope (e.g., WBS, backlog) – Monitor and validate scope |
| 9 | Integrate project planning activities | – Consolidate the project/phase plans – Assess consolidated project plans for dependencies, gaps, and continued business value – Analyze the data collected – Collect and analyze data to make informed project decisions – Determine critical information requirements |
| 10 | Manage project changes | – Anticipate and embrace the need for change (e.g., follow change management practices) – Determine strategy to handle change – Execute change management strategy according to the methodology – Determine a change response to move the project forward |
| 11 | Plan and manage procurement | – Define resource requirements and needs – Communicate resource requirements – Manage suppliers/contracts – Plan and manage procurement strategy – Develop a delivery solution |
| 12 | Manage project artifacts | – Determine the requirements (what, when, where, who, etc.) for managing the project artifacts – Validate that the project information is kept up to date (i.e., version control) and accessible to all stakeholders – Continually assess the effectiveness of the management of the project artifacts |
| 13 | Determine appropriate project methodology/methods and practices | – Assess project needs, complexity, and magnitude – Recommend project execution strategy (e.g., contracting, finance) – Recommend a project methodology/approach (i.e., predictive, agile, hybrid) – Use iterative, incremental practices throughout the project life cycle (e.g., lessons learned, stakeholder engagement, risk)14Establish project governance structure- Determine appropriate governance for a project (e.g., replicate organizational governance) – Define escalation paths and thresholds |
| 15 | Manage project issues | – Recognize when a risk becomes an issue – Attack the issue with the optimal action to achieve project success – Collaborate with relevant stakeholders on the approach to resolve the issues16Ensure knowledge transfer for project continuity- Discuss project responsibilities within team – Outline expectations for working environment – Confirm approach for knowledge transfers17Plan and manage project/phase closure or transitions- Determine criteria to successfully close the project or phase – Validate readiness for transition (e.g., to operations team or next phase) – Conclude activities to close out project or phase (e.g., final lessons learned, retrospective, procurement, financials, resources)Domain 2 – Process 50% |
Domain 3 – Business Environment 8%
| ID | Task | Enablers |
| 1 | Plan and manage project compliance | – Confirm project compliance requirements (e.g., security, health and safety, regulatory compliance) – Classify compliance categories – Determine potential threats to compliance – Use methods to support compliance – Analyze the consequences of noncompliance – Determine necessary approach and action to address compliance needs (e.g., risk, legal) – Measure the extent to which the project is in compliance |
| 2 | Evaluate and deliver project benefits and value | – Investigate that benefits are identified – Document agreement on ownership for ongoing benefit realization – Verify measurement system is in place to track benefits – Evaluate delivery options to demonstrate value – Appraise stakeholders of value gain progress |
| 3 | Evaluate and address external business environment changes for impact on scope | – Survey changes to external business environment (e.g., regulations, technology, geopolitical, market) – Assess and prioritize impact on project scope/backlog based on changes in external business environment – Recommend options for scope/backlog changes (e.g., schedule, cost changes) – Continually review external business environment for impacts on project scope/backlog |
| 4 | Support organizational change | – Assess organizational culture – Evaluate impact of organizational change to project and determine required actions – Evaluate impact of the project to the organization and determine required actions |
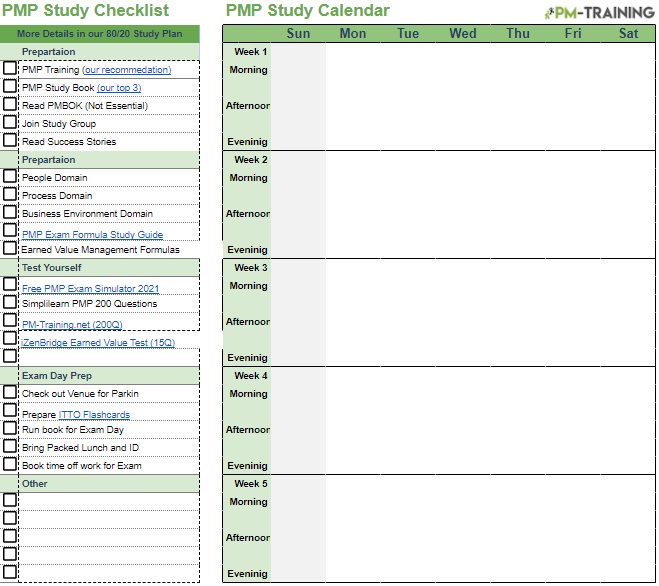
6. Have a PMP Study Checklist & Calendar
PMP Study Guide FAQ
How much does the pmp certification cost?
PMP® certification cost is not the only thing you need to take into consideration when committing to PMP© certifiaction cost. The PMP© requires a lot of effort and should not be considered a quick and easy qualification.
What are the pmp certification requirements?
The pmp certification requirements are quiet extensive as it requires formal education and a number of years experience. Bachelor’s degree or global equivalent: Minimum three years/36 months unique non-overlapping professional project management experience with 4,500 hours spent leading and directing projects. High school diploma, associate’s degree or global equivalent: Minimum five years/60 months unique non-overlapping professional project management experience and 7,500 hours spent leading and directing projects.
Estimated Budget Required for PMP
Applying for the PMP© is free but you need to meet the requirements to apply. One of the requirements is having 35 contact hours of project management. I personally had completed a Computer Management Module in Bachelors Degree so didn’t have to attend any extra classes to qualify. If you haven’t any previous project management education this is going to cost you money. To sit the actual PMP© examination its costs $405 for PMI© Members and $555 for Non-Members. To repeat the exam it costs $275 for Members and $375 for Non-Members.
PMI Project Management Formal Education for PMP
You need to make sure the course you pick goes towards formal project management education that is reconsigned by the PMI®. It is well worth checking any previous training with the instructor to see if it qualifies. There is no expiry date or a restricted time frame to have completed education hours.
If So Please Comment & Share, Thanks!
Recommended PMP Study Blog Posts
Learning Hack on How to Memorize the PMP Process Chart
I learned the PMP process chart first time round and added it to my study…
Stress Free PMP Exam Day Tips to Pass with Confidence
Fail to Prepare – Prepare to Fail – is my personal motto so do not…
Where the is pmp worth it in 2023 (Sector & Country Stats)
With the rising demand for skilled project managers, many professionals are considering the PMP Exam…
6 Reasons How Hard is PMP Exam to Pass
The Project Management Professional (PMP) exam is more challenging than other exams so you need…
PMP Experience
PMP is one of the best certificates I have ever done. It has less than…
Collection of our PMP Study Tips to Pass the PMI Exam
Top 5 Tips to Ensure you Pass the PMP Exam in 2023 on First Try
Free PMP Practice Exam Google Forms
As you start preparing for the PMP exam you need to be taking as many…
31 Free PMP Cheat sheet + Resources to Pass PMP Exam
Passing PMP can be hard and a long journey but everything worth something doesn’t come…
Earned Value Management Formulas with Examples from PMI
Measuring earned value management is an excellent way to track the progress of a project….
5 Rules to Avoid PMP Audit When Submitting a PMP Application
The PMP audit scared the crap out of me when I was applying for the…
The 7 Deadly Types of PMP Questions and Answers
The PMP questions structure is what makes the PMP exam so difficult. You have double…
Earn Free PDUs for PMP Renewal 2023
Quickly Earn Free PDUs for PMP Renewal 2022. You have 3 years before your PMP® certificateon expires….
Project Management Glossary of PMP Concepts
There are loads of terms and concepts to learn when it comes to project management…
5 Project Management Formulas PMP
Estimation in project management depends on which stage of the project. PMP has listed 6…