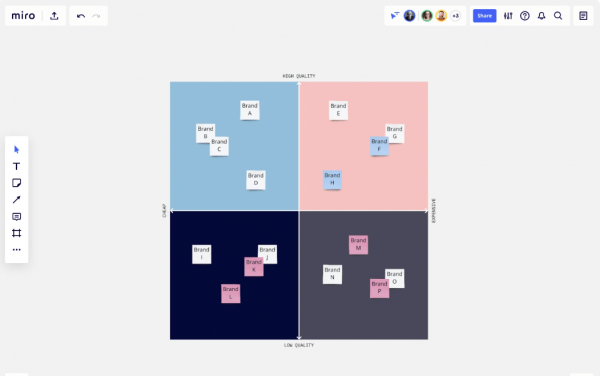
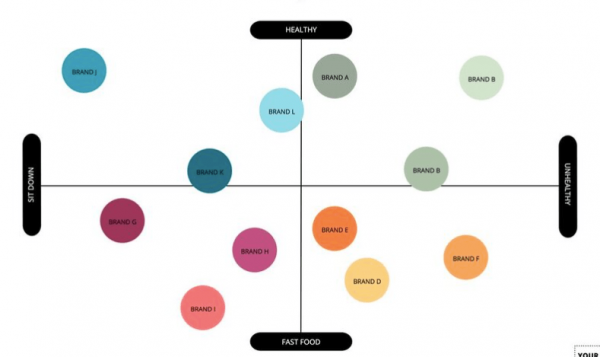
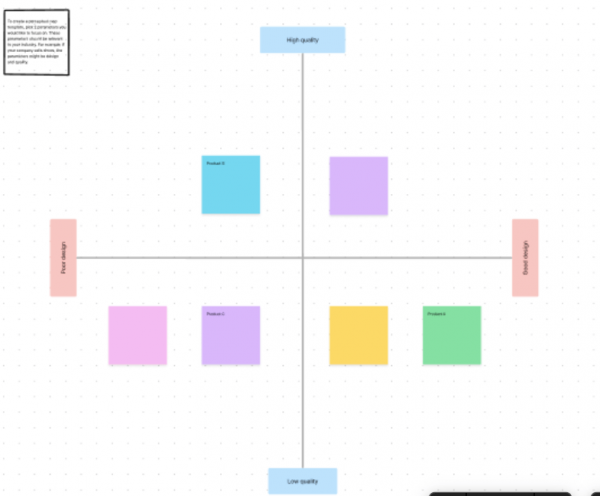
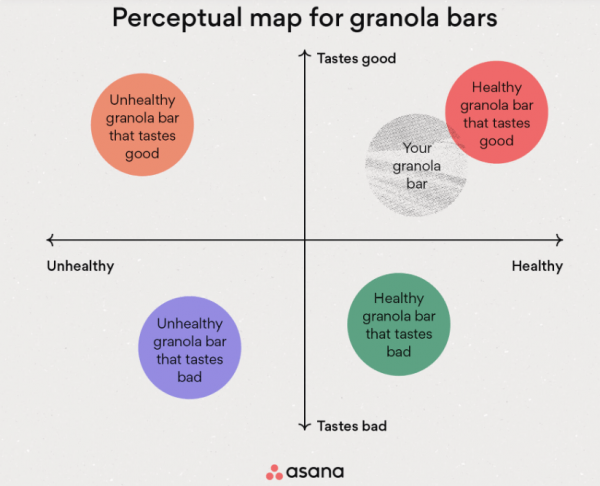
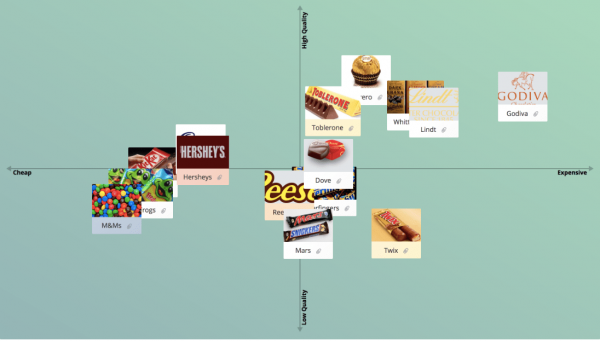
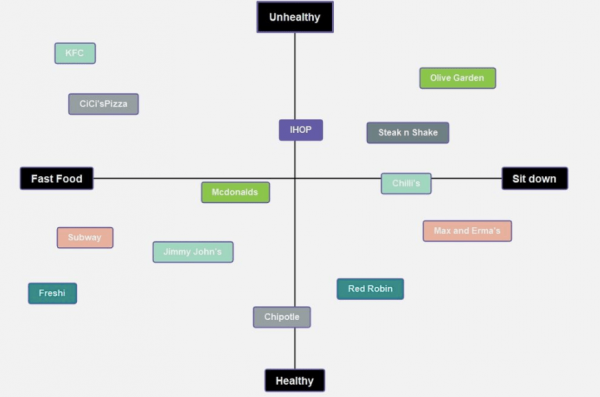
A perceptual map represents the assortment of conceptual systems that an individual might use to make sense of the world. It is designed to display the perspectives an individual has encountered, their relative importance, and how they compare with other perspectives. The basic idea behind this map is that each perspective or conceptual system operates according to its rules and thus has validity in our perception of reality.
It usually forms a grid where one axis represents time or space, and on the other axis are presented a series of concepts, people, or symbols alongside their corresponding definitions, as provided by Wikipedia. This map is good to preview a qualitative analysis once the list of topics has been identified. The map is used as a reference source to identify the most important things to discuss from a person’s viewpoint and describe how they compare with other topiaries they might use.
The critical point is to understand better their perception of the world and their ability to express that by describing their points of view. It should be used as a reference source to describe the perspective of a person and how they can express their point of view. One can use it to identify what are the most important things to discuss and how they compare with other perspectives.
One can use it in several circumstances. One can use it to filter the amount and type of information presented, which can help you better understand the context you are seeking to discuss. It can also help identify the most critical aspects to be discussed, which can be very useful when presenting information in one’s research paper or thesis.
Types of Perceptual Maps
Direct Perceptual Maps
Maps display the main dimensions of a concept resulting from an analysis (deriving topics from concepts, for example). Direct maps are convenient when the participants do not have enough experience or knowledge in the discussion area to develop their own conceptual map.
It is naturally the easiest way to get a map, but it can also be deceptive and incomplete because the participants will often only tell you what they think you want to know.
An example of this map type is on page 15 of Benvenuto (2010).
Initiative Perceptual Maps
Maps are used as a brainstorming tool where participants can freely attribute any number of points of view and relationships between them (these are usually generated using discussion). Initiative maps work well when the researcher provides little or no structure.
It allows participants to provide as much information as possible, which helps avoid the risk of missing essential data.
Deductive Perceptual Maps
Maps display new conceptual dimensions and relationships extracted from the previous analysis (determining concepts and topics from existing knowledge, for example). The deductive map is the most common in qualitative studies, with little or no prompting from the researcher.
It allows for a more in-depth analysis of an area being studied and allows participants to develop their organization to assign each point of view.
A typical example of this map type is found on page 15 of Benvenuto (2010).
Synthesizing Perceptual Maps
Maps that focus on a set of two or more concepts, attempting to synthesize them into a new concept (making a connection between two or more topics). These maps enable us to see contradictions in each set of concepts and differences that arise through comparing and contrasting different perspectives (this type of map is used when you know what you want to obtain). It is usually used with a deductive map to determine the main differences and connections between different perspectives. An example of this map type is found on page 16 of Benvenuto (2010).
Used extensively in qualitative research, they can be effective ways to create a complete understanding of an area or topic being studied. They should follow particular guidelines, mainly when used as an initial step in conducting research, and are essential for finding which aspects of your topic you want to focus on, as well as what information you need to gather that might be missing in the initial analysis.
Understanding Perceptual Map Template
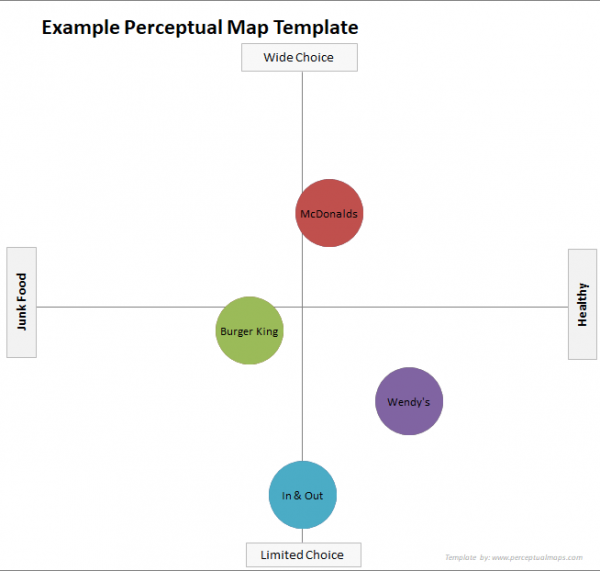
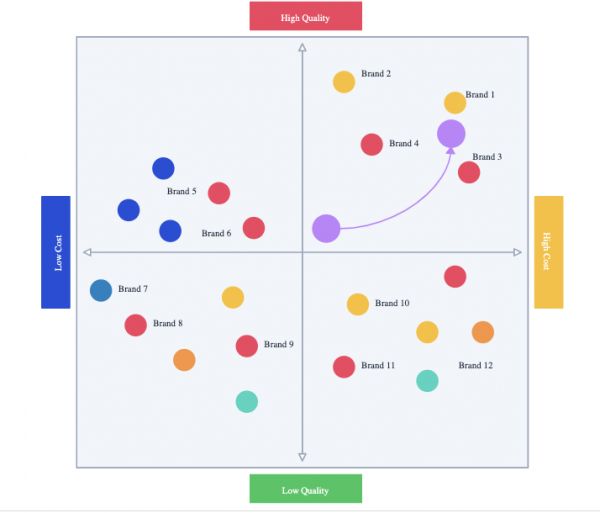
There are several different ways to create a map. One method uses a 2 x 2 layout, which creates four quadrants. The first quadrant relates to the internal world and is organized by ideas, while the second relates to the external world and is organized by situations. The third quadrant also deals with the external world, but in terms of objects rather than situations, while the fourth relates to internal structures and is organized by processes.
Another method uses three dimensions representing time or space (or both) along with objects or ideas organized in chronological or spatial order. A third method involves creating maps using two axes (the X and Y). The X axis is divided into two sections, one for internal features and processes and the other for external features and objects. Using the Y axis, each section is divided into four sections representing different relationships between the internal and external domains.
How to create a Perceptual map
Sort out the whole content in contents into one group.
Before drawing a map, try to sort out the whole content in contents into one group.
Set Dimensions
On the perceptual map template, specify the attribute dimensions in detail. The quality of the results depends on selecting the appropriate comparison dimensions, which can vary greatly amongst perceptual maps.
Brainstorm
Request a list of potential products for your market from the participants. Group-think is avoided via independent brainstorming, which also enables the facilitator to pinpoint the most typical products.
Use a whiteboard, sticky notes, or poster paper for conventional brainstorming, or a group-based internet applications. The time and effort required to gather and organize the information in subsequent steps is greatly reduced by using an online application like GroupMap.
Position
To create a visual representation of each concept’s significance in relation to one another, instruct participants to arrange each concept on the perceptual map template. This stage can be completed separately, combined, or facilitated as a group discussion, just like the brainstorming step.
Share
Prepare a report on the findings and distribute it to the appropriate stakeholders to serve as a basis for planning, decision-making, and monitoring the effectiveness of specific tactics. A perceptual map changes over time. It will alter as markets change, new goods are introduced, and trends develop.
PREMAP (Perceptual Maps) are used to show how people see things or what they think or feel about them. It is also used to show the opinions and attitudes of the target audience towards a particular brand.
When it comes to brands, PREMAPs can help them to understand their consumers’ needs and expectations in a better way so that they can stay ahead in the market. preamps are also helpful for small firms as large brands have more resources and professionals who can create new products.
They are instrumental in depicting the current status of our subject matter as they enable us to show any discrepancy between the actual state and desired state (as an example).
FAQs
What is a perceptual map used to assess?
A perceptual map assesses respondents’ subject matter, personal experience, and opinions.
What are the 2 Functions of a perceptual map?
The first function is to help students organize their ideas, while the second is to make findings visible. In this way, different stakeholders in the study can analyze and interpret them.
What must be shown on the map?
The information we want to obtain should be determined on the map. We can use different kinds of objects and ideas so that they can show the subject of our study more clearly.
Why is a perceptual map useful for brands?
Perceptual maps are helpful for brands as they can help them to see the target audience better and map their consumer needs. Perceptual maps are created with the help of various programs (such as Microsoft® Visio) that can be accessible in an easy way.
What is the difference between perceptual and position maps?
Perceptual and position maps are different. Perceptual mapping is used to analyze and understand the study subjects, while position mapping focuses on the subjects’ structural aspects. While the perceptual map is mainly used for organizing ideas and subjects, the position map is used for organizing information about structural aspects like methods, the meaning of the message, etc.