The Kano Model Analysis identifies and makes a contrast between customer and incremental requirements. Created by Noriaki Kano toward the end of the 1980s, it was developed to utilize critical thinking within these requirements.
This survey methodology for evaluation allows an analysis for a variety of functions in a product and measures them by the levels of customer satisfaction. This measurement ranges from total satisfaction to total dissatisfaction.
The Kano model is made up with several things in mind:
- Customers’ Satisfaction being contingent on a product’s features is influenced by the level of functionality
- Features are classified into one of four categories
- Questionnaires are utilized to make a determination of how customers feel about a specific feature.
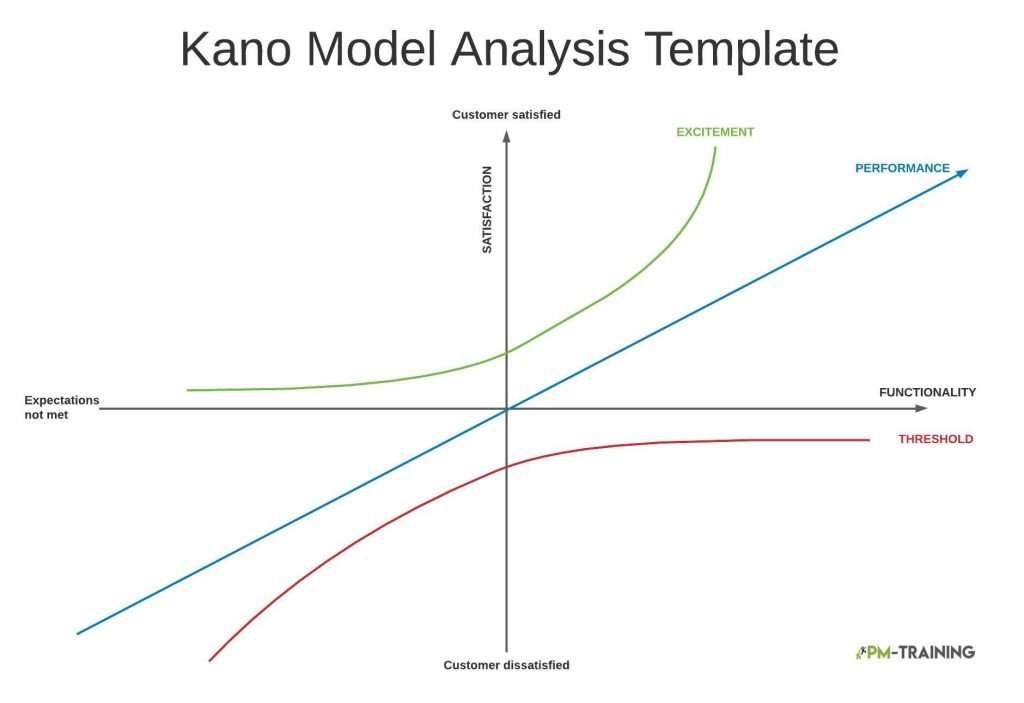
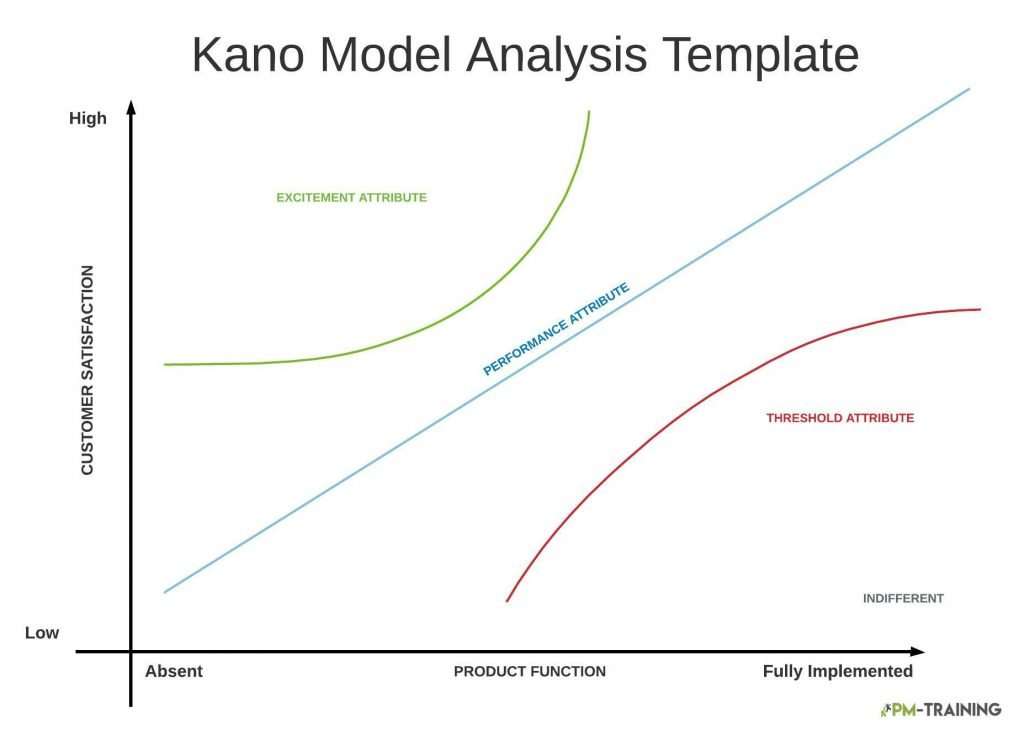
Attributes of the Kano Model Analysis
The features of a product can be classified into four categories as it relates to functionality:
- Performance
- Must-be
- Attractive
- Indifferent
When basic needs are satisfied in a product, it allows for a product to be able to position itself in a market. The satisfaction of performance needs allows for it to continue to have a place in the market, whereas fulfilling attractive needs allows for the product to gain traction as being a top leader in the market.
Performance
Performance features are classified as features that consumers expect to have in a product. Customers like its presence but dislike not having it. It correlates to a reaction of “more is better” which reflects a clear direction for a utility increase. In essence, the more that is provided, the higher customer satisfaction becomes.
Examples of features that fulfill the performance requirement
- Increased battery life for a phone
- The amount of storage a cell phone has
- Faster data speeds
Must Be
Must be features are specific requirements that needs to happen or customer will not use the product otherwise. It can also be interchanged with the term “Assumed Feature”. Due to the feature being an expectation, it doesn’t contribute to customer satisfaction. However, if the feature is not a part of the product, it would greatly contribute to a customer’s dissatisfaction.
Examples of features that fulfill the Must-Be requirement:
- A cell phone that makes phone calls
- A cell phone that has a charging port
- A cell phone that is able to use data
Attractive
Attractive features are not expected even though it is a feature that a customer would find themselves liking. These are delighting features that go past a customer’s expectations and contributes to the increase of the product’s perceived value. They are also features that separates the product from the competition.
Examples of features that fulfill the attractive requirement:
- 5G data for cell phone
- Cell Phone company offering monthly rewards to customers
- A cell phone company including hotspot in their packages
Indifferent
Indifferent of Unimportant Features creates a neutral reaction from customers regarding a product where there isn’t any emotion investment if the feature was added or taken away from the product. It is vital to not put a lot of investment into products that users are indifferent too because it doesn’t influence nor take away from a product’s value.
Examples of features that fulfill the indifferent requirement:
- The color of the charging cable
- The color of the cell phone camera lens
- The serial number for a cell phone
Note that there is room to determine “Better not be” attributes that are known to be undesirable features of a product that will create dissatisfaction in customers. They contribute to a customer finding a product less attractive regardless of whether or not they are necessary for design or safety. Undesirable feature contribute to being a reason why a customer would choose not to buy a product.
Examples of features that fulfill Undesirable attributes:
- A cell phone with minimal storage
- A cell phone that doesn’t come with a sim card
- A cell phone without data capabilities
Why Product Features Can Change
There is a dynamic to the response of features that change over time. For example, an attractive feature could turn into performance. And then that feature as performance could become a must-be feature. Meeting a must-be feature is fulfilling the bare minimum of a product’s development and will not exceed a customer’s expectations, nor will it increase customer satisfaction.
The most common way that it has occurred is with cell phones. Shifting from flip phones to touch screens were once considered exciting features for customers. Whereas now, it is a feature that is 100% expected when customers are in the market for a new phone. It would be a detrimental business move to create a cell phone that does not have a touch screen. Be mindful that customers will generally appreciate the right changes, but also it will come a time where customers will require changes.
Kano Model Benefits + Advantages
The Kano Model Analysis finds itself applicable for both solutions for consumers and non-consumers since the focus is related to identifying aspects that influence adoption of a product on a wide scale. The Kano Model positions itself as a tool that is great for analysis and identifying information and value. It gives an advantage in figuring out where to prioritize value based on what a customer may or may not want. Questions that are answered by customers determines value in the product.
Knowing what your customer wants, will prevent you from wasting resources on things that aren’t important to them.
When it comes to using the Kano Model it is important to decide on the target features that you would like to study as well as the customers that you would like to evaluate. Selecting the features should provide benefit for customers and should also be tangible. The most amount of features that you should select to prioritize is three. Taking into consideration of demographic is important in a Kano Analysis. With consumers being diverse in thought and awareness, there are risk of data being unstable without organizing them into smaller, homogenous groups. Selecting 15 or more customers for each demographic will create the most accurate results.
How to Facilitate a Kano Model Analysis Session
When distributing a Kano Model Analysis Session, it is ideal to be mindful to add a short explanation that communicates the goal of your survey and instructions that you would like for those involved to do.
Be sure to capture a way to identify your customers in the survey so that you are able to know who responded with specific answers. Google Form is an easy option for identifying your customers’ responses without having them needing to input it themselves.
It is important to ask customers clear and concise questions that represents one feature. Be sure to phrase questions in a way where customers see benefit as well as asking them about the importance of each feature presented. Interaction-based and text-based questions are the options to present in your survey.
The set of questions to ask are as follows:
- if you had (feature), how would you feel?
- If you didn’t have it, how would you feel?
- How important is having it available in your product?
Customers will be prompted to answer questions in multiple choice so that each question could be properly scored and measured. The five questions choices that customers will need to select would look like the following:
- I like this
- I must have this
- Neutral
- I’m ok with it
- I don’t like it
This will best present the wide range of satisfaction and dissatisfaction for a feature.
Taking into consideration of how various features are scored will give the best insight to classifying the feature into its correct type. For example, if a feature has customers responding neutrally when it is present, but negative in its absence, it would be best to classify that feature as assumed.
Be sure to create examples to visibly show features instead of just writing about them. Having prototypes or mockups are good replacements. Customers are able to have improvement in their understanding of a feature and it leads to less confusion.
Kano Survey Model
To avoid false positives you can send out a kano survey to your customers to find out what they really think about your product. This works well where the customers are already familiar with the product and won’t need any further information or context.
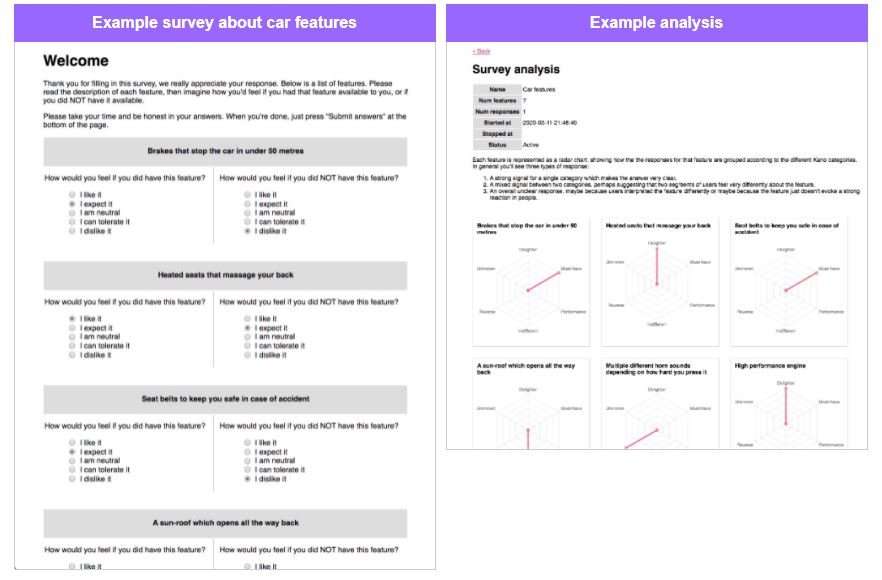
Our Kano Model Analysis Template Google
You can create a copy of this google slide by navigating here and clicking create copy
Alternate Kano Model Templates
There are a plethora of tools that can be used to develop and build your Kano Models Analysis. Finding the right platform to build your Kano Analysis is important for you and your team.
Here are some platforms that provide templates for developing a Kano model:
Miro
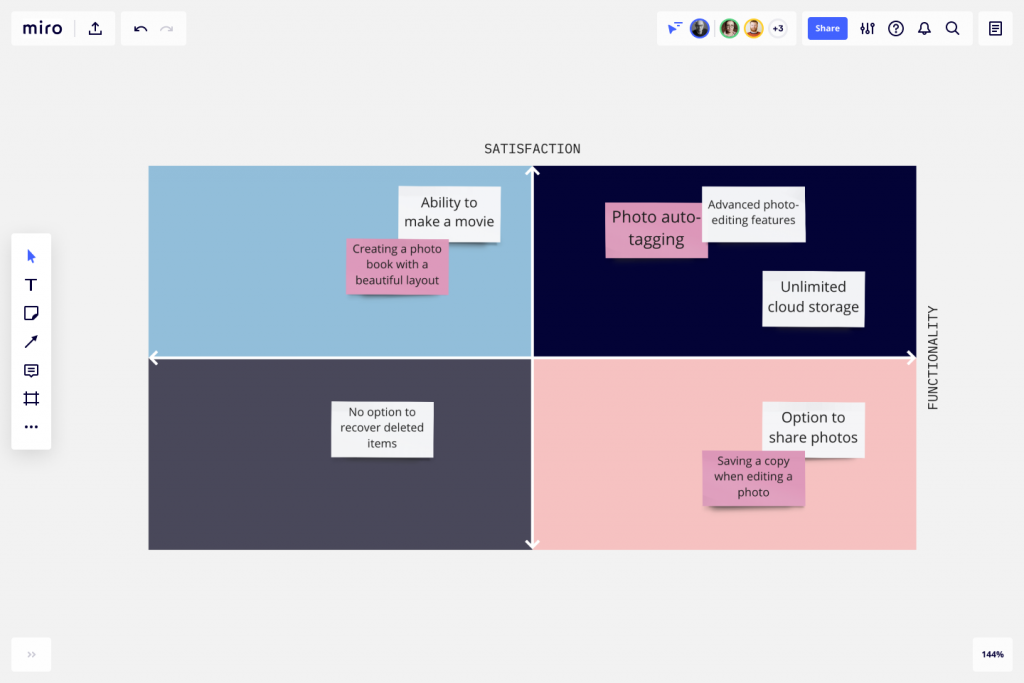
Miro is an online platform that allows for teams to collaborate through multiple formats and tools. Miro’s provision of the Kano Model Template gives the opportunity for your organization to collaborate in inputting information gathered through a Kano Model Analysis Session.
LucidChart
LucidChart provides itself as a useful tool for working with text-heavy documentation and spreadsheets. Its ability to convert them visually makes brings ease in collaborating with a team. LucidChart has a built in template that makes it easy for your team to input data.
Google Docs
Google Docs is a best-free option for your team to collaborate in developing a Kano Model. While it does not have a built in template, you are able to create one and share amongst your team and input your information in real time. Google Docs can also be used to build forms for your customers to fill out in a way that would allow for you to keep track of identifiers.
SurveyMonkey
SurveyMonkey is an exceptional platform of building your survey. Your customers will have the option to easily work through all of the questions and input additional information that you may find useful.
Alternatives to Kano Model Analysis Technique
There are popular alternatives to the Kano Model Analysis. The prioritization techniques measures the following criteria when it comes to selecting which one to use:
- Simplicity
- Data-driven prioritization
- Technology Constraints and Business Value
- Best Use Case
MoSCoW
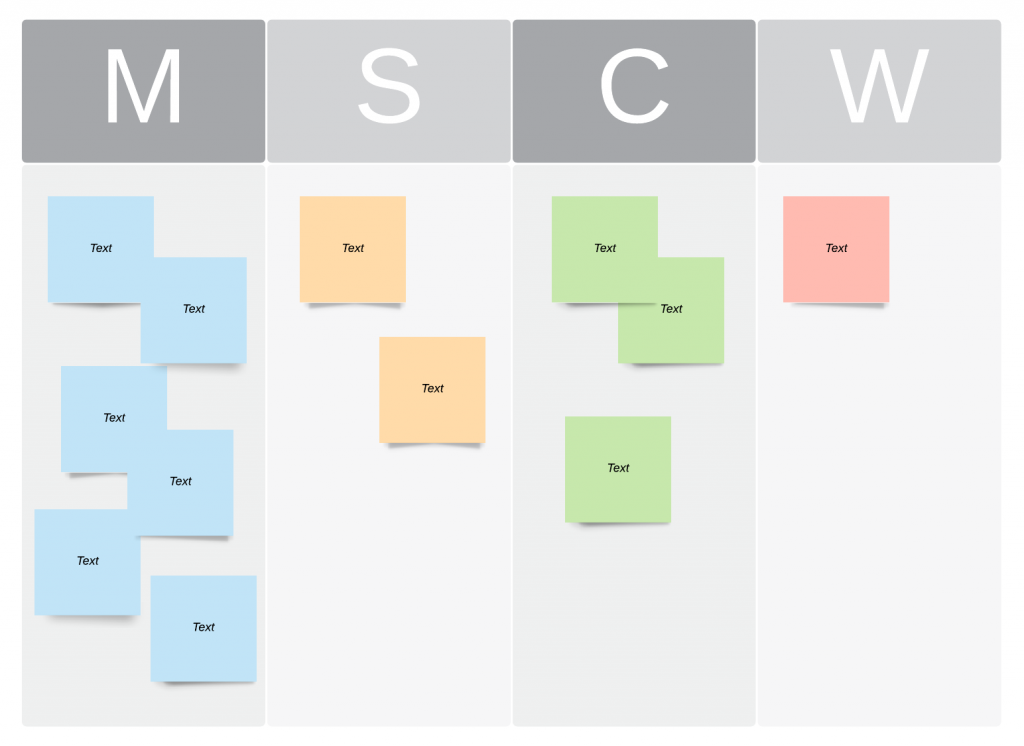
MoSCoW stands for “Must, Should, Could, Won’t” and is pioneered as being one of the most simple methods for evaluating how important each task is. The four groups that make up the acronym, are required to utilize the MoSCoW method.
>> More Info on MoSCoW Prioritization in Agile
RICE
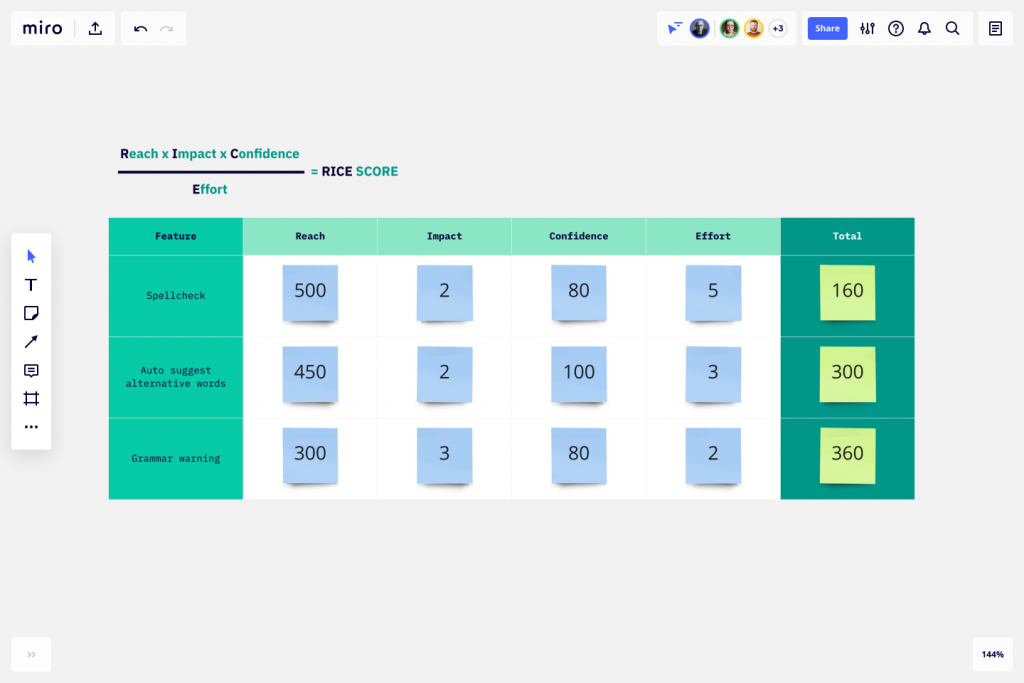
RICE which stands for Reach, Impact, Confidence, and Effort is a time-consuming methodology for evaluating customer priorities for a product. It is comprehensive in including a variety of details that allows for you to estimate success from different viewpoints.
Eisenhower Matrix
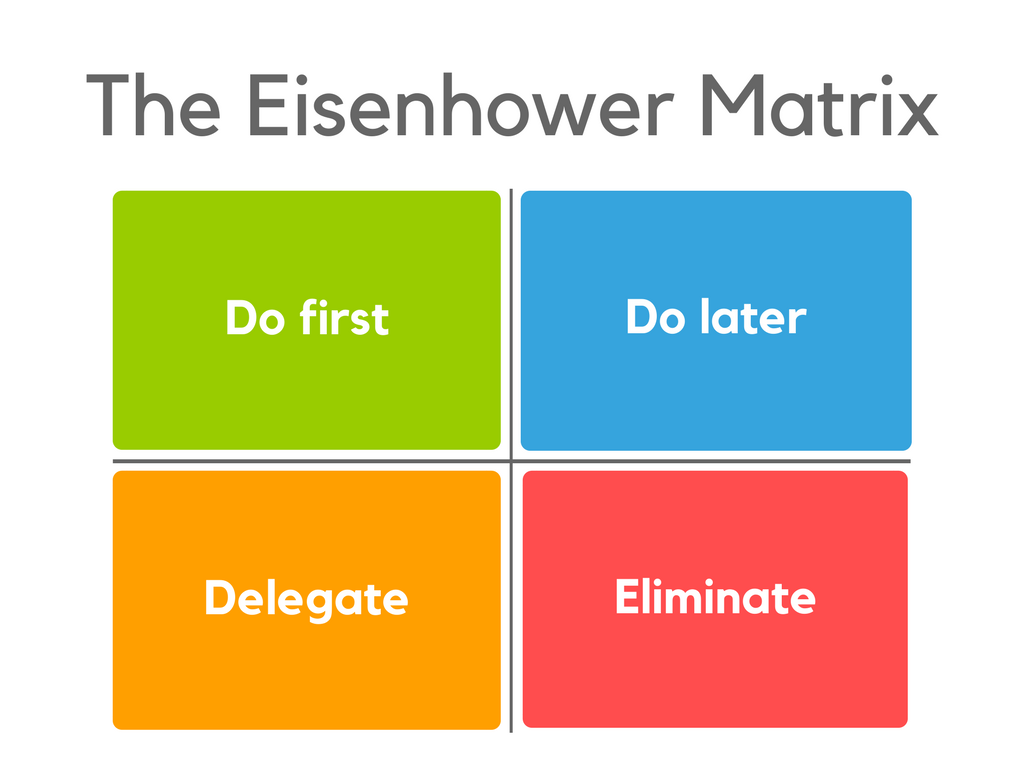
The Eisenhower Matrix is a four-quadrant technique that is used to prioritize tasks that are backlogged. Each quadrant of the matrix represents where each task is to be allocated.
- High Priority
- Medium Priority
- Urgent but not Important
- Low Priority
Value vs Complexity/Effort
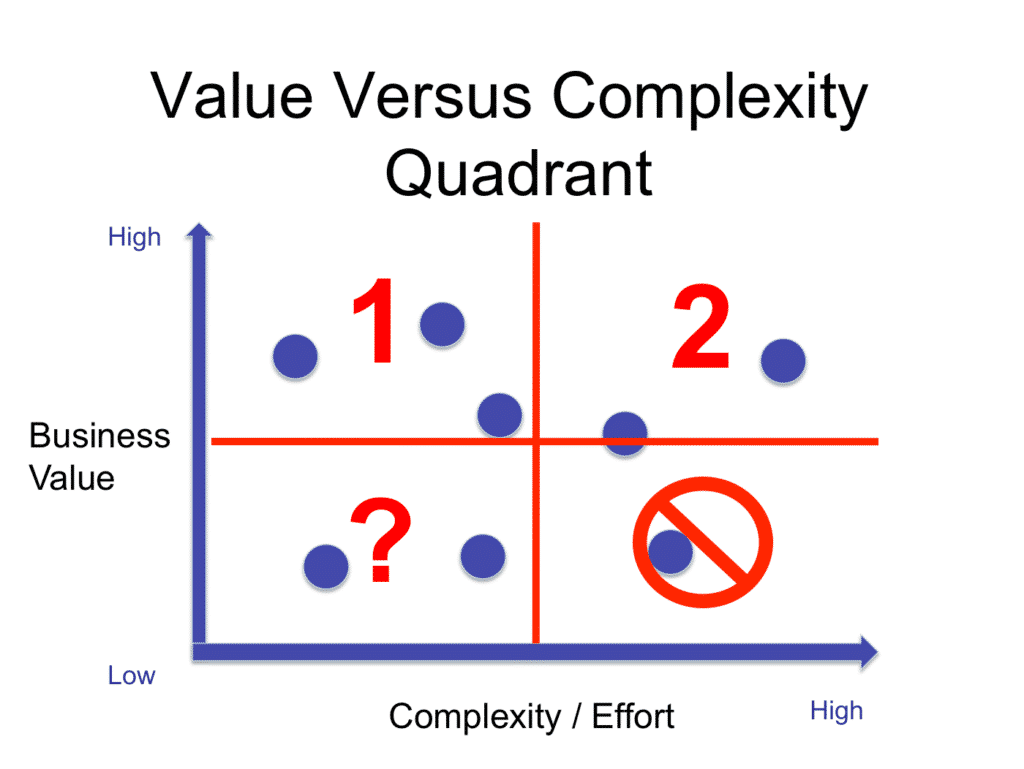
The Value vs Complexity/Effort Matrix is similar to the Eisenhower Matrix where tasks are allocated throughout four quadrants through two dimensions. The prioritized tasks are those that are high in value, but low in complexity.
WSJF
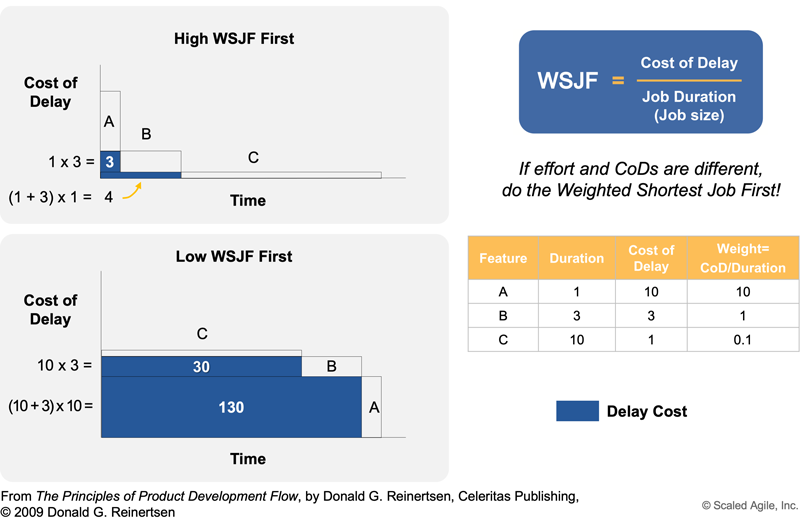
WSJF, which represents Weighted Shortest Job First is a time-consuming method for introducing the minimum level of marketable features of a product. This measurement specifically orders to place high added-value into non-comprehensive features for top priority and complicated features that have lesser value towards the bottom.
Walking Skeleton
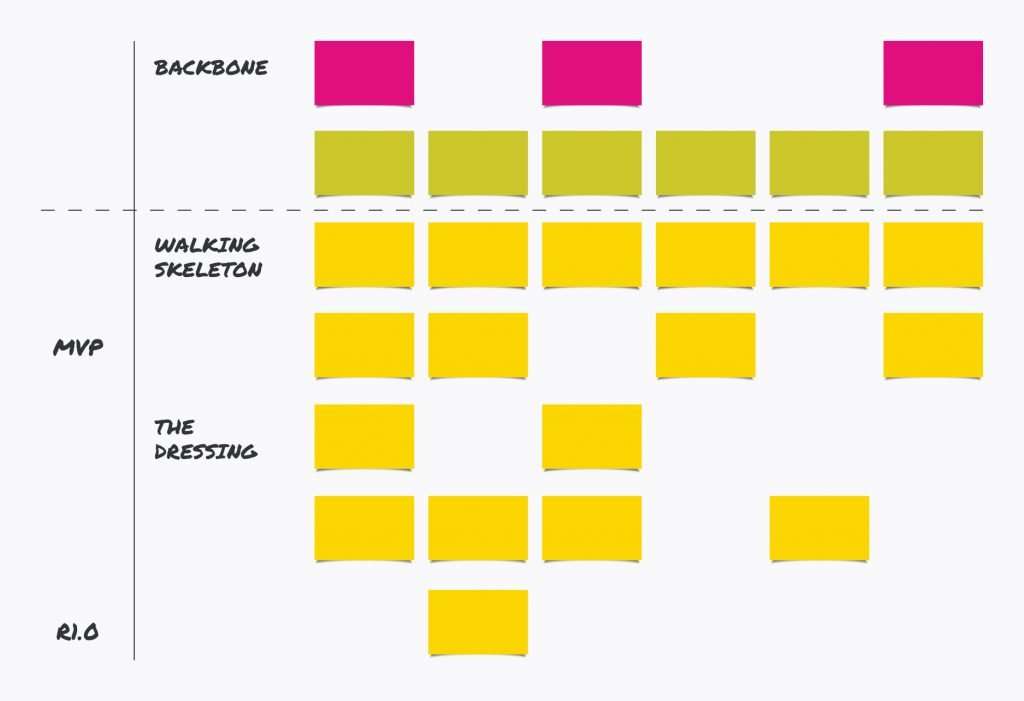
The Walking Skeleton defines which features are vital for the functionality of a product. While it doesn’t put requirements in categories, it focuses on user report which prioritizes key features, functionality for a system, business value, and testing of the entire production.
