Data Governance is a framework designed to ensure that data is consistently managed and controlled throughout an organization. It includes policies and procedures for managing data, as well as processes for ensuring that data is accurate, reliable, and accessible.
It is the process of ensuring that project data is accurate, consistent, and compliant with organizational standards. This includes the development of policies and procedures for managing project data, as well as the implementation of those policies and procedures.
There are many benefits of implementing an Agile data governance strategy, such as improved data quality, better decision-making, and reduced costs. However, the most important benefit is that it helps organizations to be more agile and responsive to change. For Project Managers, it helps to ensure that the data used in a project is of high quality.
This, in turn, can help to improve the accuracy of project reports and ensure that the project stays on track. Additionally, it can help to prevent data breaches and other security risks.

Why is Data Governance Strategy Needed for Organizations?
Without a data governance strategy in place, organizations run the risk of making changes to data that could have negative consequences.
For example, if data is not properly controlled, it could be modified in a way that violates regulatory requirements. Or, if data is not consistently updated, it could become inaccurate, which could lead to decision-makers making incorrect decisions based on that data.
A data governance strategy helps to avoid these risks by establishing processes and controls for how data should be managed. By doing so, organizations can ensure that data is properly governed throughout the Agile process.
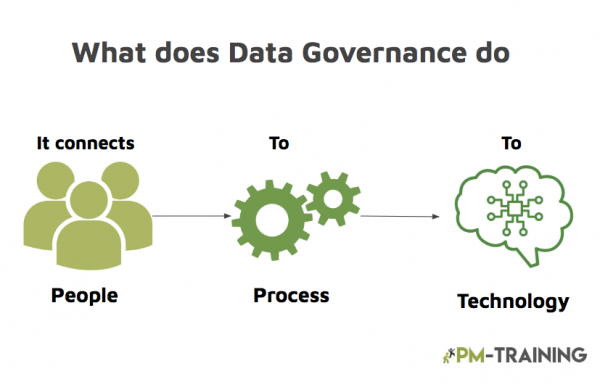
Why is Data Governance important for Project Managers?
It provides a structure for managing project data. It can help project managers to avoid data silos, ensure that data is consistently maintained, and make it easier to share project data with stakeholders.
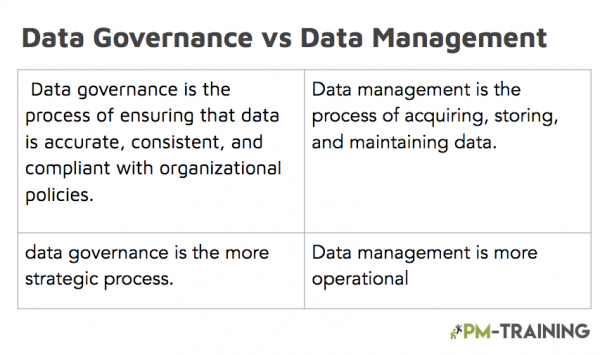
Data Governance vs Data Management
In order to have effective data governance, organizations need to have well-defined data management processes in place. Without these processes, it would be difficult to govern data in a consistent and controlled manner.
The terms “data management” and “data governance” are often used interchangeably, but they are two distinct concepts.
5 steps when implementing a data governance strategy
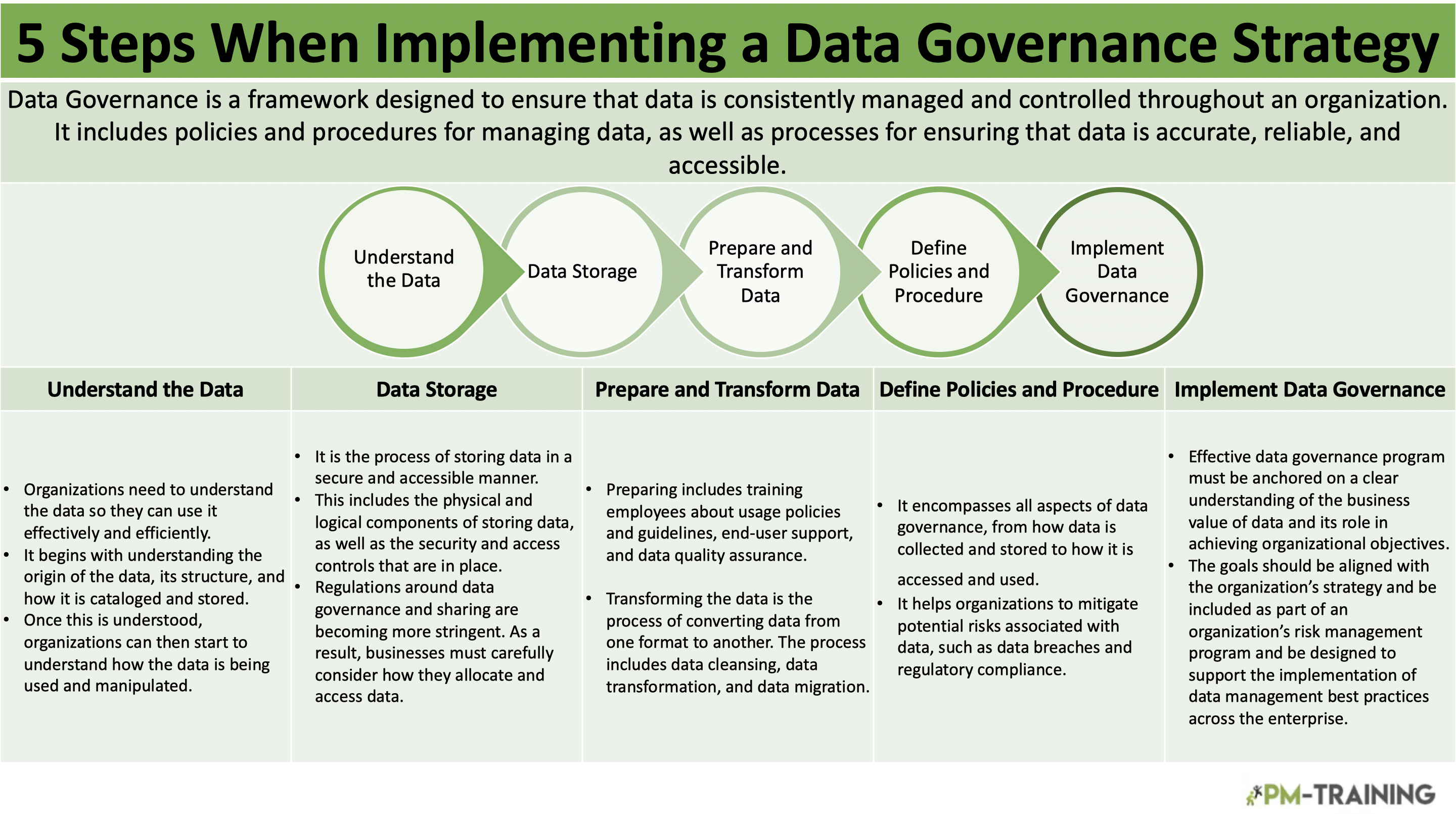
Organizations must have well-defined processes and procedures in place for managing their data. Data governance can be complex, but there are a few key things that project managers should keep in mind.
Understand the Data you have
Basically, prioritize and identify. In order to make sure that data is being used effectively and efficiently, organizations need to understand the data they have.
This process begins with understanding the origin of the data, its structure, and how it is cataloged and stored. Once this is understood, organizations can then start to understand how the data is being used and manipulated.
Data Storage
Data storage is a critical part of any organization’s data governance strategy. It is the process of storing data in a secure and accessible manner.
This includes the physical and logical components of storing data, as well as the security and access controls that are in place.
With the proliferation of cloud-based applications and the increased use of mobile devices, businesses are generating more data than ever before.
At the same time, regulations around data governance and sharing are becoming more stringent. As a result, businesses must carefully consider how they allocate and access data.
Preparing and transforming the data
This process includes training employees about usage policies and guidelines, end-user support, and data quality assurance.
This is a critical part of any organization’s strategy for managing data.
For example, employee onboarding is the process of providing new or existing employees with the necessary training and resources to perform their job. It includes orienting employees to the company’s culture, values, and goals. It also provides training on the company’s policies and procedures.
Also, transforming the data is the process of converting data from one format to another. The process includes data cleansing, data transformation, and data migration.
Defining Policies and Procedures
It encompasses all aspects of data governance, from how data is collected and stored to how it is accessed and used.
This is important because it helps organizations to mitigate potential risks associated with data, such as data breaches and regulatory compliance. It can also create potential risks for organizations if not properly implemented.
For example, data governance can give individuals excess access to data, which can lead to security risks and also create privacy risks if individuals do not have the appropriate security controls in place.
Implementing Data Governance
An effective data governance roadmap program must be anchored on a clear understanding of the business value of data and its role in achieving organizational objectives. The goals should be aligned with the organization’s strategy and be included as part of an organization’s risk management program and be designed to support the implementation of data management best practices across the enterprise.
For example, a Data Management Roadmap provides a guide for implementing data governance in phases, starting with the establishment of policies and procedures.
The roadmap outlines the key tasks and deliverables for each phase of the data governance implementation.
When implementing data governance is to preparing and transforming the Metadata is important to establish the Data Governance Council. The Data Governance Council is responsible for approving the Data Governance Framework and for setting the direction in the enterprise.
Defensive vs Offensive data strategy
A company’s ability to collect, process, and use data can make the difference between success and failure. As such, it’s important for companies to have a data strategy that covers both offensive and defensive aspects.
Offensive Data Strategy
An offensive data strategy focuses on how a company can use data to gain a competitive advantage. This could involve using data to develop new products or services, to target new markets, or improve operational efficiency.
Defensive Data Strategy
A defensive data strategy, on the other hand, focuses on how a company can protect its data from being misused or stolen by competitors. This could involve encryption, access control, and other security measures.
Data Governance Strategy Roadmap
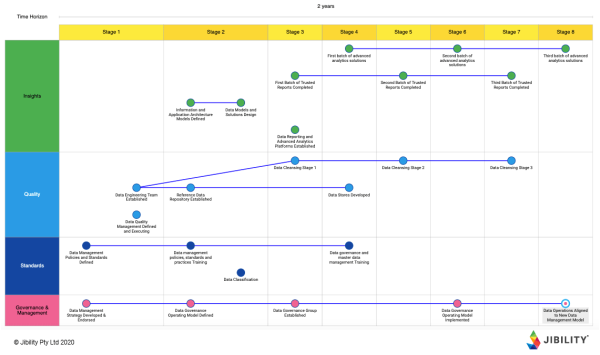
Data Governance Roadmap Example — A Strategic Approach | Jibility
Different scenarios of Data Governance
Financial Institutions
Financial institutions such as banks, firms, companies, and similar; face a number of challenges when it comes to data governance.
This is because the sheer volume of data that they generate and collect is enormous and they must comply with a variety of regulations that govern the use of data.
Thus, banks must protect customer data from being leaked or stolen. In the world of finance, data governance is the set of policies, procedures, and people that work together to protect and ensure the accuracy of an organization’s data. A well-designed program can improve data quality, reduce financial risks, and increase operational efficiency.
Health Care Institutions
In a hospital, there are numerous types of data that are generated and used on a daily basis.
This data includes patient medical records, laboratory results, radiology images, and more. With so much data being generated and used, it is important to have a system in place to ensure that it is managed properly. This is where data governance comes in.
For example, in any given year, one in four hospital patients will experience a medical error. This staggering statistic is just one indication of how important it is for hospitals to have a robust data governance policy in place.
This data can include patient medical records, financial data, and more preventing data breaches and protecting the privacy of patients.
