Top-notch project managers understand the importance of the communication process. Aspiring project managers need to know and understand this process, as it is a fundamental soft skill required in the workplace. In fact, central to the whole managing process is the ability to carefully and effectively convey important information.
In this blog post, we will discuss the communication process diagram process, why it is crucial, and the different variations of it. By the end of this blog, you will clearly understand how the communication process works and how you can use it in your future career as a project manager.

Why is Communication Important?
Communication skills are essential for aspiring project managers as they must effectively communicate with their team members, clients, and stakeholders. Good communication skills can help to build trust, resolve conflict and create a positive working environment.
Clear and concise communication can help to reduce misunderstandings and improve productivity levels within a team. Developing strong communication skills should be a key focus for anyone looking to pursue a career in project management.
Osmotic communication is also important because it creates a greater sense of sharing and collaboration among team members as it is more informal and allows team members to share ideas more easily.
What is the Communication Process?
The communication process refers to the transfer of information or message from a sender via a chosen medium to a receiver, overcoming any obstacles that impede its speed.
The communication process involves eight core steps that are necessary for effective communication. These steps are sender, encoding, message, medium, receiver, decoding, feedback, and context.
Diagram of The Communication Process Model
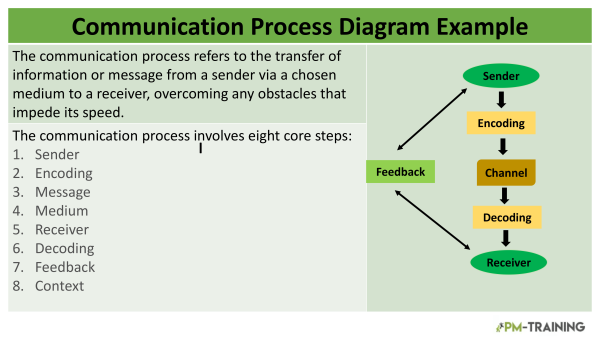
Sender
The sender is someone who initiates the communication. The sender is initially responsible for the message’s success. Their experiences, attitudes, knowledge, skill, perceptions, and culture impact the message.
Encoding
Encoding is the process of translating the sender’s thoughts into a form that can be transmitted via a chosen medium. Examples of mediums can be verbal, nonverbal, or written.
Message
The message is the information conveyed by words, either spoken or written, as well as signs, pictures, or symbols. It is the essence of communication as it is the information that the sender wishes to send.

Medium
It is the channel where a message is transmitted. Some examples of the medium are email, face-to-face conversation, and phone calls.
Receiver
The receiver is the one who receives and interprets the message. Decoding is translating the received message back into thoughts so the receiver can understand it.
Feedback
Feedback is the end of the process of communication. The receiver responds to a message and conveys that response to the sender after it has been received. The sender cannot confirm that the receiver has interpreted the message correctly without feedback.
7-Step Communication Process Model Variation
There are 7 step variations to the communication process. While all are very similar, the 7 step adds two critical components to the communication process: decoding and context.

Decoding
From the receiver’s end of the message, the facility of how they decode or interpret the message is just as important. The capacity to do this depends on a couple of critical factors.
The first will be if they have any bias that may hinder their ability to see the message objectively. Secondly, the receiver’s level of knowledge will play a role. Giving a message to a receiver unfamiliar with the topic can have a different interpretation compared to the understanding of someone who knows the subject.
Context
Context is the final and possibly most important part of the 7-step communication process. Context refers to everything that surrounds communication. It includes but is not limited to: place, time, culture, noise level, body language, etc. All of these factors play a role in the interpretation of the message.
Practical Application of the Communication Process Diagram in Project Management
In project management, the communication process is the process of planning, executing, and monitoring communications among project stakeholders.
The purpose of the communication process is to ensure that all stakeholders have the information they need to make decisions and take the actions necessary for the project’s successful completion.
There are four types of communication in project management: verbal, written, visual, and electronic.
- Verbal communication: face-to-face meetings, conference calls, and webinars.
- Written communication: emails, memos, reports, and presentations.
- Visual communication: charts, diagrams, and infographics.
- Electronic communication includes text messages, instant messages, and social media posts.

The communication process begins with the project manager identifying the stakeholders who need to be involved in the project. The project manager then develops a communication plan that outlines how and when each stakeholder will receive information. The communication plan should identify who will be responsible for each task in the communication process.
Once the communication plan is in place, the project manager and other stakeholders will begin to execute the plan. During execution, it is vital to monitor communications to ensure that all stakeholders receive the information they need.
If any project changes or information need to be communicated, the project manager should update the communication plan accordingly.
The communication process is an integral part of project management because it ensures that all stakeholders are informed about the project and that they have the opportunity to provide input.
By following a structured process, project managers can ensure that everyone has the same understanding of the project and its objectives. It can help to avoid confusion and conflict among stakeholders and ultimately lead to a successful outcome.
